Dermatopathic Lymphadenitis
- PMID: 26609001
- PMCID: PMC4795245
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.169172
Dermatopathic Lymphadenitis
Figures
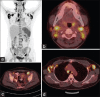
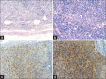
References
-
- Makis W, Hickeson M, Blumenkrantz M. Interesting image. Dermatopathic lymphadenitis: A pitfall for lymphoma evaluation by F-18 FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2010;35:872–4. - PubMed
-
- Acipayam C, Kupeli S, Sezgin G, Acikalin A, Ozkan A, Inan DA, et al. Dermatopathic lymphadenitis associated with human papilloma virus infection and verruca vulgaris. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;36:e231–3. - PubMed
-
- Steffen C. Frédéric Woringer: Pautrier-Woringer disease (lipomelanotic reticulosis/dermatopathic lymphadenitis) Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26:499–503. - PubMed
-
- Psarommatis I, Vontas H, Gkoulioni V, Mihail-Strantzia A, Bairamis T. Dermatopathic lymphadenitis imitating a deep neck space infection. Am J Otolaryngol. 2009;30:419–22. - PubMed
-
- Good DJ, Gascoyne RD. Atypical lymphoid hyperplasia mimicking lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:729–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

