A Tetrameric Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibits Specific Cytotoxic Effects against Oral Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 26609531
- PMCID: PMC4644816
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/630179
A Tetrameric Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibits Specific Cytotoxic Effects against Oral Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
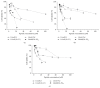
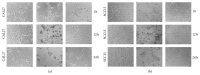
Several short linear peptides derived from cyclic bovine lactoferricin were synthesized and tested for their cytotoxic effect against the oral cavity squamous-cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines CAL27 and SCC15. As a control, an immortalized and nontumorigenic cell line, Het-1A, was used. Linear peptides based on the RRWQWR core sequence showed a moderate cytotoxic effect and specificity towards tumorigenic cells. A tetrameric peptide, LfcinB(20-25)4, containing the RRWQWR motif, exhibited greater cytotoxic activity (>90%) in both OSCC cell lines compared to the linear lactoferricin peptide or the lactoferrin protein. Additionally, this tetrameric peptide showed the highest specificity towards tumorigenic cells among the tested peptides. Interestingly, this effect was very fast, with cell shrinkage, severe damage to cell membrane permeability, and lysis within one hour of treatment. Our results are consistent with a necrotic effect rather than an apoptotic one and suggest that this tetrameric peptide could be considered as a new candidate for the therapeutic treatment of OSCC.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Synthetic Peptides Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibit Cytotoxic Effect against MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Molecules. 2017 Sep 29;22(10):1641. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101641. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28961215 Free PMC article.
-
A tetrameric peptide derived from bovine lactoferricin as a potential therapeutic tool for oral squamous cell carcinoma: A preclinical model.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174707. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358840 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer activities of bovine and human lactoferricin-derived peptides.Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;95(1):91-98. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0175. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28165293
-
Effect of Polyvalence on the Antibacterial Activity of a Synthetic Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin against Healthcare-Associated Infectious Pathogens.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 10;2018:5252891. doi: 10.1155/2018/5252891. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29984236 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Peptides Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibit Antimicrobial Activity against E. coli ATCC 11775, S. maltophilia ATCC 13636 and S. enteritidis ATCC 13076.Molecules. 2017 Mar 12;22(3):452. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030452. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28287494 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synergistic bactericide and antibiotic effects of dimeric, tetrameric, or palindromic peptides containing the RWQWR motif against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 5;9(13):7239-7245. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00708c. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35519960 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides Derived from (RRWQWRMKKLG)2-K-Ahx Induce Selective Cellular Death in Breast Cancer Cell Lines through Apoptotic Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 26;21(12):4550. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124550. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32604743 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of breast cancer xenografts in a mouse model and the induction of apoptosis in multiple breast cancer cell lines by lactoferricin B peptide.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7181-7189. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16748. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34236134 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Synthetic Peptides Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibit Cytotoxic Effect against MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Molecules. 2017 Sep 29;22(10):1641. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101641. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28961215 Free PMC article.
-
Application Value of Antimicrobial Peptides in Gastrointestinal Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16718. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316718. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hill B. T., Price L. A. Lack of survival advantage in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to local therapy, despite achieving an initial high clinical complete remission rate. American Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1994;17(1):1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

