A Tetrameric Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibits Specific Cytotoxic Effects against Oral Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 26609531
- PMCID: PMC4644816
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/630179
A Tetrameric Peptide Derived from Bovine Lactoferricin Exhibits Specific Cytotoxic Effects against Oral Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
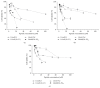
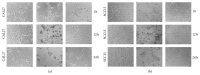
Several short linear peptides derived from cyclic bovine lactoferricin were synthesized and tested for their cytotoxic effect against the oral cavity squamous-cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines CAL27 and SCC15. As a control, an immortalized and nontumorigenic cell line, Het-1A, was used. Linear peptides based on the RRWQWR core sequence showed a moderate cytotoxic effect and specificity towards tumorigenic cells. A tetrameric peptide, LfcinB(20-25)4, containing the RRWQWR motif, exhibited greater cytotoxic activity (>90%) in both OSCC cell lines compared to the linear lactoferricin peptide or the lactoferrin protein. Additionally, this tetrameric peptide showed the highest specificity towards tumorigenic cells among the tested peptides. Interestingly, this effect was very fast, with cell shrinkage, severe damage to cell membrane permeability, and lysis within one hour of treatment. Our results are consistent with a necrotic effect rather than an apoptotic one and suggest that this tetrameric peptide could be considered as a new candidate for the therapeutic treatment of OSCC.
Figures





References
-
- Hill B. T., Price L. A. Lack of survival advantage in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to local therapy, despite achieving an initial high clinical complete remission rate. American Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1994;17(1):1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

