Resveratrol as a Bioenhancer to Improve Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Apigenin
- PMID: 26610561
- PMCID: PMC4663613
- DOI: 10.3390/nu7115485
Resveratrol as a Bioenhancer to Improve Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Apigenin
Abstract
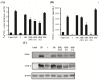
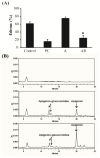
The aim of this study was to improve the anti-inflammatory activities of apigenin through co-treatment with resveratrol as a bioenhancer of apigenin. RAW 264.7 cells pretreated with hepatic metabolites formed by the co-metabolism of apigenin and resveratrol (ARMs) in HepG2 cells were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). ARMs prominently inhibited (p < 0.05) the production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E₂ (PGE₂), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α. Otherwise no such activity was observed by hepatic metabolites of apigenin alone (AMs). ARMs also effectively suppressed protein expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Co-administration of apigenin (50 mg/kg) and resveratrol (25 mg/kg) also showed a significant reduction of carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice (61.20% to 23.81%). Co-administration of apigenin and resveratrol led to a 2.39 fold increase in plasma apigenin levels compared to administration of apigenin alone, suggesting that co-administration of resveratrol could increase bioavailability of apigenin. When the action of resveratrol on the main apigenin metabolizing enzymes, UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), was investigated, resveratrol mainly inhibited the formation of apigenin glucuronides by UGT1A9 in a non-competitive manner with a Ki value of 7.782 μM. These results suggested that resveratrol helps apigenin to bypass hepatic metabolism and maintain apigenin's anti-inflammatory activities in the body.
Keywords: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT); anti-inflammation; bioenhancer; hepatic metabolites of apigenin.
Figures



References
-
- Nicholas C., Batra S., Vargo M.A., Voss O.H., Gavrilin M.A., Wewers M.D., Guttridge D.C., Grotewold E., Doseff A.I. Apigenin blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality in vivo and proinflammatory cytokines expression by inactivating NF-kappaB through the suppression of p65 phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2007;179:7121–7127. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.7121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bose K.C. Pharmacopoeia India: Being a Collection of Vegetable, Mineral (and) Animal Drugs in Common Use in India. The Book Co.; Calcutta, India: 1932.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

