Defining A-Kinase Anchoring Protein (AKAP) Specificity for the Protein Kinase A Subunit RI (PKA-RI)
- PMID: 26611881
- PMCID: PMC4836982
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201500632
Defining A-Kinase Anchoring Protein (AKAP) Specificity for the Protein Kinase A Subunit RI (PKA-RI)
Abstract
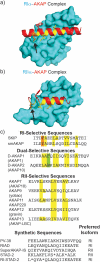
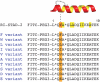
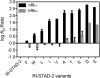
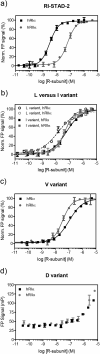
A-Kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) act as spatial and temporal regulators of protein kinase A (PKA) by localizing PKA along with multiple proteins into discrete signaling complexes. AKAPs interact with the PKA holoenzyme through an α-helix that docks into a groove formed on the dimerization/docking domain of PKA-R in an isoform-dependent fashion. In an effort to understand isoform selectivity at the molecular level, a library of protein-protein interaction (PPI) disruptors was designed to systematically probe the significance of an aromatic residue on the AKAP docking sequence for RI selectivity. The stapled peptide library was designed based on a high affinity, RI-selective disruptor of AKAP binding, RI-STAD-2. Phe, Trp and Leu were all found to maintain RI selectivity, whereas multiple intermediate-sized hydrophobic substitutions at this position either resulted in loss of isoform selectivity (Ile) or a reversal of selectivity (Val). As a limited number of RI-selective sequences are currently known, this study aids in our understanding of isoform selectivity and establishing parameters for discovering additional RI-selective AKAPs.
Keywords: A-kinase anchoring protein; cAMP signaling; isoforms; protein kinase A; selectivity; stapled peptides.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- Taylor SS, Yang J, Wu J, Haste NM, Radzio-Andzelm E, Anand G. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1697:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Sarma GN, Kinderman FS, Kim C, von Daake S, Chen L, Wang BC, Taylor SS. Structure. 2010;18:155–166. - PMC - PubMed
- Kinderman FS, Kim C, von Daake S, Ma Y, Pham BQ, Spraggon G, Xuong NH, Jennings PA, Taylor SS. Mol Cell. 2006;24:397–408. - PMC - PubMed
- Gold MG, Lygren B, Dokurno P, Hoshi N, McConnachie G, Tasken K, Carlson CR, Scott JD, Barford D. Mol Cell. 2006;24:383–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

