Separation of parallel encoded complex-valued slices (SPECS) from a single complex-valued aliased coil image
- PMID: 26612076
- PMCID: PMC4761326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2015.11.003
Separation of parallel encoded complex-valued slices (SPECS) from a single complex-valued aliased coil image
Abstract
Purpose: Achieving a reduction in scan time with minimal inter-slice signal leakage is one of the significant obstacles in parallel MR imaging. In fMRI, multiband-imaging techniques accelerate data acquisition by simultaneously magnetizing the spatial frequency spectrum of multiple slices. The SPECS model eliminates the consequential inter-slice signal leakage from the slice unaliasing, while maintaining an optimal reduction in scan time and activation statistics in fMRI studies.
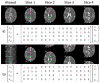
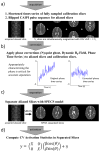
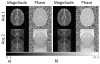
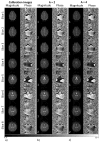
Materials and methods: When the combined k-space array is inverse Fourier reconstructed, the resulting aliased image is separated into the un-aliased slices through a least squares estimator. Without the additional spatial information from a phased array of receiver coils, slice separation in SPECS is accomplished with acquired aliased images in shifted FOV aliasing pattern, and a bootstrapping approach of incorporating reference calibration images in an orthogonal Hadamard pattern.
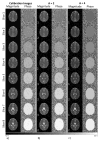
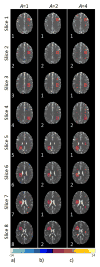
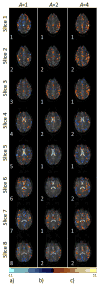
Result: The aliased slices are effectively separated with minimal expense to the spatial and temporal resolution. Functional activation is observed in the motor cortex, as the number of aliased slices is increased, in a bilateral finger tapping fMRI experiment.
Conclusion: The SPECS model incorporates calibration reference images together with coefficients of orthogonal polynomials into an un-aliasing estimator to achieve separated images, with virtually no residual artifacts and functional activation detection in separated images.
Keywords: MRI; Multiband; Parallel slice; SPECS; Simultaneous multi-slice (SMS); fMRI.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimization of hyperparameters for SMS reconstruction.Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Nov;73:91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.08.006. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32835848
-
A circular echo planar sequence for fast volumetric fMRI.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Mar;81(3):1685-1698. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27522. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30273963 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration (CAIPIRINHA) for multi-slice imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2005 Mar;53(3):684-91. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20401. Magn Reson Med. 2005. PMID: 15723404
-
Recent advances in parallel imaging for MRI.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017 Aug;101:71-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 2. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 28844222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receive coil arrays and parallel imaging for functional magnetic resonance imaging of the human brain.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;2006:17-20. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.259560. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17946771 Review.
Cited by
-
Autobiography of James S. Hyde.Appl Magn Reson. 2017 Dec;48(11-12):1103-1147. doi: 10.1007/s00723-017-0950-5. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Appl Magn Reson. 2017. PMID: 29962662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sodickson DK, Manning WJ. Simultaneous Acquisition of Spatial Harmonics (SMASH): Fast Imaging with Radiofrequency Coil Arrays. Magn Reson Med. 1997;4:591–603. - PubMed
-
- Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: Sensitivity Encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42:952–962. - PubMed
-
- Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA) Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:1202–1210. - PubMed
-
- Muller S. Multifrequency selective RF pulses for multislice MR imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1998;6:364–371. - PubMed
-
- Souza SP, Szumowski J, Dumoulin CL, Plewes DP, Glover G. SIMA: simultaneous multislice acquisition of MR images by Hadamard-encoded excitation. Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988;12:1026–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

