Functional Dependence and Mortality in the International Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS)
- PMID: 26612280
- PMCID: PMC5530761
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.09.024
Functional Dependence and Mortality in the International Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS)
Abstract
Background: Patients receiving long-term dialysis have among the highest mortality and hospitalization rates. In the nonrenal literature, functional dependence is recognized as a contributor to subsequent disability, recurrent hospitalization, and increased mortality. A higher burden of functional dependence with progressive worsening of kidney function has been observed in several studies, suggesting that functional dependence may contribute to both morbidity and mortality in dialysis patients.
Study design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting & participants: 7,226 hemodialysis patients from 12 countries in the DOPPS (Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study) phase 4 (2009-2011) with self-reported data for functional status.
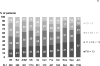
Predictor: Patients' ability to perform 13 basic and instrumental activities of daily living was summarized to create an overall functional status score (range, 1.25 [most dependent] to 13 [functionally independent]).
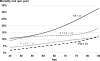
Outcome: Cox regression was used to estimate the association between functional status and all-cause mortality, adjusting for several demographic and clinical risk factors for mortality. Median follow-up was 17.2 months.
Results: The proportion of patients who could perform each activity of daily living task without assistance ranged from 97% (eating) to 47% (doing housework). 36% of patients could perform all 13 tasks without assistance (functional status = 13), and 14% of patients had high functional dependence (functional status < 8). Functionally independent patients were younger and had many indicators of better health status, including higher quality of life. Compared with functionally independent patients, the adjusted HR for mortality was 2.37 (95% CI, 1.92-2.94) for patients with functional status < 8.
Limitations: Possible nonresponse bias and residual confounding.
Conclusions: We found a high burden of functional dependence across all age groups and across all DOPPS countries. When adjusting for several known mortality risk factors, including age, access type, cachexia, and multimorbidity, functional dependence was a strong consistent predictor of mortality.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease (CKD); Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS); activity of daily living (ADL); dialysis; end-stage renal disease (ESRD); functional dependence; functional status; hospitalization; independence; morbidity; mortality; physical activity; quality of life (QoL).
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures

References
-
- USRDS. Chapter 3: Hospitalization. 2013 http://www.usrds.org/2013/pdf/v2_ch3_13.pdf last accessed 6 August 2015.
-
- Ariyaratne TV, Ademi Z, Duffy SJ, Andrianopoulos N, Billah B, Brennan AL, et al. Cardiovascular readmissions and excess costs following percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with chronic kidney disease: data from a large multi-centre Australian registry. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:2783–2790. - PubMed
-
- Sands LP, Xu H, Craig BA, Eng C, Covinsky KE. Predicting change in functional status over quarterly intervals for older adults enrolled in the PACE community-based long-term care program. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2008;20:419–427. - PubMed
-
- Carey EC, Covinsky KE, Lui LY, Eng C, Sands LP, Walter LC. Prediction of mortality in community-living frail elderly people with long-term care needs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:68–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

