Novel candidate genes AuxRP and Hsp90 influence the chip color of potato tubers
- PMID: 26612975
- PMCID: PMC4648990
- DOI: 10.1007/s11032-015-0415-1
Novel candidate genes AuxRP and Hsp90 influence the chip color of potato tubers
Abstract
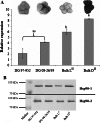
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers exhibit significant variation in reducing sugar content directly after harvest, cold storage and reconditioning. Here, we performed QTL analysis for chip color, which is strongly influenced by reducing sugar content, in a diploid potato mapping population. Two QTL on chromosomes I and VI were detected for chip color after harvest and reconditioning. Only one region on chromosome VI was linked with cold-induced sweetening. Using the RT-PCR technique, we showed differential expression of the auxin-regulated protein (AuxRP) gene. The AuxRP transcript was presented in light chip color parental clone DG 97-952 and the RNA progeny of the bulk sample consisting of light chip color phenotypes after cold storage. This amplicon was absent in dark chip parental clone DG 08-26/39 and the RNA bulk sample of dark chip progeny. Genetic variation of AuxRP explained up to 16.6 and 15.2 % of the phenotypic variance after harvest and 3 months of storage at 4 °C, respectively. Using an alternative approach, the RDA-cDNA method was used to recognize 25 gene sequences, of which 11 could be assigned to potato chromosome VI. One of these genes, Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90), demonstrated higher mRNA and protein expression in RT-qPCR and western blotting assays in the dark chip color progeny bulk sample compared with the light chip color progeny bulk sample. Our study, for the first time, suggests that the AuxRP and Hsp90 genes are novel candidate genes capable of influencing the chip color of potato tubers.
Keywords: Auxin-regulated protein (AuxRP) gene; DArT markers; Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) gene; Quantitative trait loci; Reducing sugar content; Solanum tuberosum.
Figures


References
-
- Chen X, Salamini F, Gebhardt C. A potato molecular-function map for carbohydrate metabolism and transport. Theor Appl Genet. 2001;102:284–295. doi: 10.1007/s001220051645. - DOI
-
- Cunningham CE, Stevenson FJ. Inheritance of factors affecting potato chip color and their association with specific gravity. Am Potato J. 1963;40:253–265. doi: 10.1007/BF02850325. - DOI
-
- Douches DS, Freyre R. Identification of genetic factors influencing chip color in diploid potato (Solanum spp.) Am Potato J. 1994;71:581–590. doi: 10.1007/BF02851523. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

