Delineation of MGMT Hypermethylation as a Biomarker for Veliparib-Mediated Temozolomide-Sensitizing Therapy of Glioblastoma
- PMID: 26615020
- PMCID: PMC4862419
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv369
Delineation of MGMT Hypermethylation as a Biomarker for Veliparib-Mediated Temozolomide-Sensitizing Therapy of Glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Sensitizing effects of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitors have been studied in several preclinical models, but a clear understanding of predictive biomarkers is lacking. In this study, in vivo efficacy of veliparib combined with temozolomide (TMZ) was evaluated in a large panel of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) patient-derived xenografts (PDX) and potential biomarkers were analyzed.
Methods: The efficacy of TMZ alone vs TMZ/veliparib was compared in a panel of 28 GBM PDX lines grown as orthotopic xenografts (8-10 mice per group); all tests of statistical significance were two-sided. DNA damage was analyzed by γH2AX immunostaining and promoter methylation of DNA repair gene O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) by Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-approved methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction.
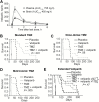
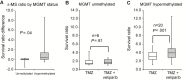
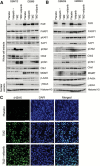
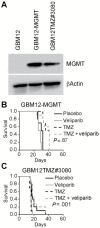
Results: The combination of TMZ/veliparib statistically significantly extended survival of GBM models (P < .05 by log-rank) compared with TMZ alone in five of 20 MGMT-hypermethylated lines (average extension in median survival = 87 days, range = 20-150 days), while the combination was ineffective in six MGMT-unmethylated lines. In the MGMT promoter-hypermethylated GBM12 line (median survival with TMZ+veliparib = 189 days, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 59 to 289 days, vs TMZ alone = 98 days, 95% CI = 49 to 210 days, P = .04), the profound TMZ-sensitizing effect of veliparib was lost when MGMT was overexpressed (median survival with TMZ+veliparib = 36 days, 95% CI = 28 to 38 days, vs TMZ alone = 35 days, 95% CI = 32 to 37 days, P = .87), and a similar association was observed in two nearly isogenic GBM28 sublines with an intact vs deleted MGMT locus. In comparing DNA damage signaling after dosing with veliparib/TMZ or TMZ alone, increased phosphorylation of damage-responsive proteins (KAP1, Chk1, Chk2, and H2AX) was observed only in MGMT promoter-hypermethylated lines.
Conclusion: Veliparib statistically significantly enhances (P < .001) the efficacy of TMZ in tumors with MGMT promoter hypermethylation. Based on these data, MGMT promoter hypermethylation is being used as an eligibility criterion for A071102 (NCT02152982), the phase II/III clinical trial evaluating TMZ/veliparib combination in patients with GBM.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Liu X, Han EK, Anderson M, et al. Acquired resistance to combination treatment with temozolomide and ABT-888 is mediated by both base excision repair and homologous recombination DNA repair pathways. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7 (10):1686–1692. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese CR, Almassy R, Barton S, et al. Anticancer chemosensitization and radiosensitization by the novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor AG14361. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96 (1):56–67. - PubMed
-
- Thomas HD, Calabrese CR, Batey MA, et al. Preclinical selection of a novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor for clinical trial. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6 (3):945–956. - PubMed
-
- Miknyoczki S, Chang H, Grobelny J, et al. The selective poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1(2) inhibitor, CEP-8983, increases the sensitivity of chemoresistant tumor cells to temozolomide and irinotecan but does not potentiate myelotoxicity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6 (8):2290–2302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

