Parental Restriction of Mature-rated Media and Its Association With Substance Use Among Argentinean Adolescents
- PMID: 26615087
- PMCID: PMC4821658
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acap.2015.11.004
Parental Restriction of Mature-rated Media and Its Association With Substance Use Among Argentinean Adolescents
Abstract
Objective: To assess the independent relation between parental restrictions on mature-rated media (M-RM) and substance use among South American adolescents.
Methods: Cross-sectional school-based youth survey of 3,172 students (mean age, 12.8 years; 57.6% boys) in 3 large Argentinean cities. The anonymous survey queried tobacco, alcohol, and drug use using items adapted from global youth surveys. Adolescents reported M-RM restriction for internet and video game use, television programming, and movies rated for adults. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to assess the association between parental M-RM restriction and substance use after adjustment for hourly media use, measures of authoritative parenting style, sociodemographic characteristics, and sensation-seeking.
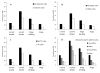
Results: Substance use rates were 10% for current smoking, 32% for current drinking alcohol, 17% for past 30-day binge drinking, and 8% for illicit drug use (marijuana or cocaine). Half of the respondents reported parental M-RM restriction (internet 52%, TV 43%, adult movies 34%, video game 25%). Parental M-RM restriction was only modestly correlated with authoritative parenting measures. In multivariate analyses M-RM restriction on all 4 venues was strongly protective for all substance use outcomes. Compared with no restriction, odds ratios for substance use for full restrictions were 0.32 (0.18-0.59), 0.53 (0.38-0.07), 0.36 (0.22-0.59), and 0.49 (0.26-0.92) for current smoking, drinking, binge drinking, and illicit drug use, respectively. The most important single M-RM venue was movies.
Conclusions: Results of this study confirmed the protective association between parental M-RM restriction during adolescence and multiple substance use outcomes, including illicit drugs. M-RM restriction is independent of traditional parenting measures. The preponderance of the evidence supports intervention development.
Keywords: alcohol; drugs; media; parenting; prevention; tobacco; youth.
Copyright © 2016 Academic Pediatric Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parental Style and Its Association With Substance Use in Argentinean Youth.Subst Use Misuse. 2017 Mar 21;52(4):518-526. doi: 10.1080/10826084.2016.1245337. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Subst Use Misuse. 2017. PMID: 28010167 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between parental restrictions on movies and adolescent use of tobacco and alcohol.Eff Clin Pract. 2002 Jan-Feb;5(1):1-10. Eff Clin Pract. 2002. PMID: 11874190
-
Association between television, movie, and video game exposure and school performance.Pediatrics. 2006 Oct;118(4):e1061-70. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-2854. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 17015499
-
Social Inequality and Substance Use and Problematic Gambling Among Adolescents and Young Adults: A Review of Epidemiological Surveys in Germany.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2016;9(1):26-48. doi: 10.2174/1874473709666151209114023. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2016. PMID: 26647784 Review.
-
Drinking Over the Lifespan: Focus on Early Adolescents and Youth.Alcohol Res. 2016;38(1):95-101. Alcohol Res. 2016. PMID: 27159816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Remote Acculturation and Cigarette Smoking Susceptibility among Youth in Mexico.J Cross Cult Psychol. 2019 Jan;50(1):63-79. doi: 10.1177/0022022118807578. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Cross Cult Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31223173 Free PMC article.
-
Demographic, physical and mental health assessments in the adolescent brain and cognitive development study: Rationale and description.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2018 Aug;32:55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29113758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF E-CIGARETTE TRIAL AMONG ADOLESCENTS IN ARGENTINA.Tob Prev Cessat. 2016 Dec;2:80. doi: 10.18332/tpc/66950. Tob Prev Cessat. 2016. PMID: 31355353 Free PMC article.
-
Why are Spanish Adolescents Binge Drinkers? Focus Group with Adolescents and Parents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 19;17(10):3551. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103551. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32438735 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking susceptibility as a predictive measure of cigarette and e-cigarette use among early adolescents.Salud Publica Mex. 2018 Jul-Aug;60(4):423-431. doi: 10.21149/9193. Salud Publica Mex. 2018. PMID: 30137944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumrind D. The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. Journal of Early Adolescent. 1991;11:56–95.
-
- Laugesen M, Scragg R, Wellman RJ, DiFranza JR. R-rated film viewing and adolescent smoking. Preventive medicine. 2007;45:454–459. - PubMed
-
- Sargent JD. Effect of Parental R-Rated Movie Restriction on Adolescent Smoking Initiation: A Prospective Study. Pediatrics. 2004;114:149–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

