Isolation and Identification of Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing-Related Micro-RNAs by Functionalized Silicon Nanowire Field-effect Transistor
- PMID: 26616332
- PMCID: PMC4663627
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17375
Isolation and Identification of Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing-Related Micro-RNAs by Functionalized Silicon Nanowire Field-effect Transistor
Abstract
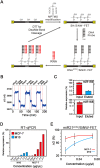
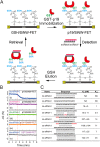
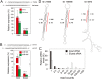
Many transcribed RNAs are non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), which bind to complementary sequences on messenger RNAs to regulate the translation efficacy. Therefore, identifying the miRNAs expressed in cells/organisms aids in understanding genetic control in cells/organisms. In this report, we determined the binding of oligonucleotides to a receptor-modified silicon nanowire field-effect transistor (SiNW-FET) by monitoring the changes in conductance of the SiNW-FET. We first modified a SiNW-FET with a DNA probe to directly and selectively detect the complementary miRNA in cell lysates. This SiNW-FET device has 7-fold higher sensitivity than reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction in detecting the corresponding miRNA. Next, we anchored viral p19 proteins, which bind the double-strand small RNAs (ds-sRNAs), on the SiNW-FET. By perfusing the device with synthesized ds-sRNAs of different pairing statuses, the dissociation constants revealed that the nucleotides at the 3'-overhangs and pairings at the terminus are important for the interactions. After perfusing the total RNA mixture extracted from Nicotiana benthamiana across the device, this device could enrich the ds-sRNAs for sequence analysis. Finally, this bionanoelectronic SiNW-FET, which is able to isolate and identify the interacting protein-RNA, adds an additional tool in genomic technology for the future study of direct biomolecular interactions.
Figures
References
-
- Hannon G. J. RNA interference. Nature 418, 244–251 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Tomari Y. & Zamore P. D. Perspective: machines for RNAi. Gene Dev. 19, 517–529 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wu H.-W., Lin S.-S., Chen K.-C., Yeh S.-D. & Chua N.-H. Discriminating mutations of HC-Pro of zucchini yellow mosaic virus with differential effects on small RNA pathways involved in viral pathogenicity and symptom development. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 23, 17–28 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Wu R.-M., Wood M., Thrush A., Walton E. F. & Varkonyi-Gasic E. Real-Time PCR quantification of plant miRNAs using Universal ProbeLibrary Technology. Biochemica 2, 12–15 (2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

