The Role of Platelet-Activating Factor in Chronic Inflammation, Immune Activation, and Comorbidities Associated with HIV Infection
- PMID: 26616844
- PMCID: PMC5056589
The Role of Platelet-Activating Factor in Chronic Inflammation, Immune Activation, and Comorbidities Associated with HIV Infection
Abstract
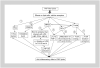
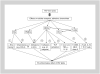
With the advent of highly effective antiretroviral therapy, cardiovascular disease has become an important cause of morbidity and mortality among people with treated HIV-1, but the pathogenesis is unclear. Platelet-activating factor is a potent lipid mediator of inflammation that has immunomodulatory effects and a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders and cardiovascular disease. Limited scientific evidence suggests that the platelet-activating factor pathway may be a mechanistic link between HIV-1 infection, systemic inflammation, and immune activation that contribute to pathogenesis of chronic HIV-related comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease and HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. In this review, we examine the mechanisms by which the cross-talk between HIV-1, immune dysregulation, inflammation, and perturbations in the platelet-activating factor pathway may directly affect HIV-1 immunopathogenesis. Understanding the role of platelet-activating factor in HIV-1 infection may pave the way for further studies to explore therapeutic interventions, such as diet, that can modify platelet-activating factor activity and use of platelet-activating factor inhibitors that might improve the prognosis of HIV-1 infected patients.
Figures


References
-
- Guaraldi G, Orlando G, Zona S, et al. Premature age-related comorbidities among HIV-infected persons compared with the general population. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:1120–6. - PubMed
-
- Tsimikas S, Miller YI. Oxidative modification of lipoproteins: mechanisms, role in inflammation and potential clinical applications in cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK, Hermansson A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:204–12. - PubMed
-
- Frostegard J, Huang YH, Ronnelid J, Schafer-Elinder L. Platelet-activating factor and oxidized LDL induce immune activation by a common mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:963–8. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DH, Taub DD. Inhibition of chemokine receptor function by membrane cholesterol oxidation. Exp Cell Res. 2003;291:36–45. - PubMed

