Intermedin attenuates myocardial infarction through activation of autophagy in a rat model of ischemic heart failure via both cAMP and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways
- PMID: 26617693
- PMCID: PMC4637778
Intermedin attenuates myocardial infarction through activation of autophagy in a rat model of ischemic heart failure via both cAMP and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways
Abstract
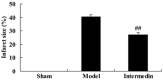
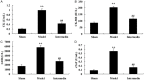
Intermedin is a proopiomelanocortin-derived peptide before opioid promoting cortical hormone, its main function embodies in mononuclear macrophages and neutrophilic granulocytes to inhibit the proinflammatory cytokines. The aim of this study is to determine intermedin attenuates myocardial infarction and its related mechanisms in a rat model of ischemic heart failure. After rat model of ischemic heart failure was set up, myocardial infarction, blood levels of activities of creatine kinase (CK), the MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and cardiac troponin T (cTnT) were effectively reduced by treatment with intermedin. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in a rat model of ischemic heart failure were recovered by pretreatment with intermedin. Administrate of intermedin availably promoted cAMP contents and suppressed caspase-3 protein in ischemic heart failure rat. ERK1/2 and LC3 protein expression were significantly activated and autophagy was significantly promoted by intermedin in a rat model of ischemic heart failure. These results indicate that intermedin protected rat heart, attenuates myocardial infarction from ischemic heart failure in the rat model. The underlying mechanisms may include upregulation of cAMP, ERK1/2 and LC3 protein expression and activating of autophagy.
Keywords: ERK1/2; Intermedin; autophagy; cAMP; ischemic heart failure.
Figures






References
-
- Choi JH, Comess KA, Xu C, Park J, Kim Y. Development of an interactive Coronary Doppler Vibrometry system for detection of coronary artery disease. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;2011:7195–7198. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Wang W, Gong F, Fu S, Zhang Q, Hu J, Qi Y, Xie C, Zhang Y. Evaluation of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in relation to Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in patients with Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:805–814. - PubMed
-
- Bi YF, Mao JY, Wang XL, Hou YZ, Lu YZ, Soh SB, Zhang BL. Clinical epidemiology survey of the traditional Chinese medicine etiology and syndrome differentiation of coronary artery disease: study protocol of a multicenter trial. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012;10:619–627. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Xu B, Yang YJ, Zhang RY, Li JP, Qiao SB, Zhang JS, Hu J, Qin XW, Hong T, Chen JL, Huo Y, Shen WF, Gao RL. Sirolimus-eluting cobalt alloyed stents in treating patients with coronary artery disease: six-month angiographic and one-year clinical follow-up result. A prospective, historically controlled, multi-center clinical study. Chin Med J (Engl) 2007;120:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Burchill LJ, Lameijer H, Roos-Hesselink JW, Grewal J, Ruys TP, Kulikowski JD, Burchill LA, Oudijk MA, Wald RM, Colman JM, Siu SC, Pieper PG, Silversides CK. Pregnancy risks in women with pre-existing coronary artery disease, or following acute coronary syndrome. Heart. 2015;101:525–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
