Chronic Heart Failure Follow-up Management Based on Agent Technology
- PMID: 26618038
- PMCID: PMC4659889
- DOI: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.307
Chronic Heart Failure Follow-up Management Based on Agent Technology
Abstract
Objectives: Monitoring heart failure patients through continues assessment of sign and symptoms by information technology tools lead to large reduction in re-hospitalization. Agent technology is one of the strongest artificial intelligence areas; therefore, it can be expected to facilitate, accelerate, and improve health services especially in home care and telemedicine. The aim of this article is to provide an agent-based model for chronic heart failure (CHF) follow-up management.
Methods: This research was performed in 2013-2014 to determine appropriate scenarios and the data required to monitor and follow-up CHF patients, and then an agent-based model was designed.
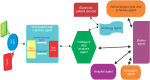
Results: Agents in the proposed model perform the following tasks: medical data access, communication with other agents of the framework and intelligent data analysis, including medical data processing, reasoning, negotiation for decision-making, and learning capabilities.
Conclusions: The proposed multi-agent system has ability to learn and thus improve itself. Implementation of this model with more and various interval times at a broader level could achieve better results. The proposed multi-agent system is no substitute for cardiologists, but it could assist them in decision-making.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Health Information Systems; Heart Failure; Multi-agent Systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Sahay A, Kapoor JR, Pham MX, Massie B. Divergent trends in survival and readmission following a hospitalization for heart failure in the Veterans Affairs health care system 2002 to 2006. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(5):362–368. - PubMed
-
- Koehler F, Winkler S, Schieber M, Sechtem U, Stangl K, Bohm M, et al. Impact of remote telemedical management on mortality and hospitalizations in ambulatory patients with chronic heart failure: the telemedical interventional monitoring in heart failure study. Circulation. 2011;123(17):1873–1880. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WT, Adamson PB, Bourge RC, Aaron MF, Costanzo MR, Stevenson LW, et al. Wireless pulmonary artery haemodynamic monitoring in chronic heart failure: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9766):658–666. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources