Aqueous Tear Deficiency Increases Conjunctival Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) Expression and Goblet Cell Loss
- PMID: 26618646
- PMCID: PMC4669202
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.15-17627
Aqueous Tear Deficiency Increases Conjunctival Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) Expression and Goblet Cell Loss
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the hypothesis that increased interferon-γ (IFN-γ) expression is associated with conjunctival goblet cell loss in subjects with tear dysfunction.
Methods: Goblet cell density (GCD) was measured in impression cytology from the temporal bulbar conjunctiva, and gene expression was measured in cytology samples from the nasal bulbar conjunctiva obtained from 68 subjects, including normal control, meibomian gland disease (MGD), non-Sjögren syndrome (non-SSATD)-, and Sjögren syndrome (SSATD)-associated aqueous tear deficiency. Gene expression was evaluated by real-time PCR. Tear meniscus height (TMH) was measured by optical coherence tomography. Fluorescein and lissamine green dye staining evaluated corneal and conjunctival disease, respectively. Between-group mean differences and correlation coefficients were calculated.
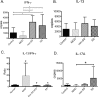
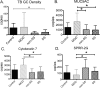
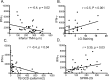
Results: Compared to control, IFN-γ expression was significantly higher in both ATD groups, and its receptor was higher in SSATD. Expression of IL-13 and its receptor was similar in all groups. Goblet cell density was lower in the SSATD group; expression of MUC5AC mucin was lower and cornified envelope precursor small proline-rich region (SPRR)-2G higher in both ATD groups. Interferon-γ transcript number was inversely correlated with GCD (r = -0.37, P < 0.04) and TMH (r = -0.37, P = 0.02), and directly correlated with lissamine green staining (r = 0.51, P < 0.001) and SPRR-2G expression (r = 0.32, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Interferon-γ expression in the conjunctiva was higher in aqueous deficiency and correlated with goblet cell loss and severity of conjunctival disease. These results support findings of animal and culture studies showing that IFN-γ reduces conjunctival goblet cell number and mucin production.
Figures
References
-
- Pflugfelder SC,, Huang AJ,, Feuer W,, Chuchovski PT,, Pereira IC,, Tseng SC. Conjunctival cytologic features of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97: 985–991. - PubMed
-
- Pflugfelder SC,, Tseng SC,, Yoshino K,, Monroy D,, Felix C,, Reis BL. Correlation of goblet cell density and mucosal epithelial membrane mucin expression with rose bengal staining in patients with ocular irritation. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104: 223–235. - PubMed
-
- Nelson JD,, Wright JC. Conjunctival goblet cell densities in ocular surface disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984; 102: 1049–1051. - PubMed
-
- Tatematsu Y,, Ogawa Y,, Shimmura S,, et al. Mucosal microvilli in dry eye patients with chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012; 47: 416–425. - PubMed
-
- De Paiva CS,, Villarreal AL,, Corrales RM,, et al. Dry eye-induced conjunctival epithelial squamous metaplasia is modulated by interferon-gamma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48: 2553–2560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

