Nanoconnectomic upper bound on the variability of synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 26618907
- PMCID: PMC4737657
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10778
Nanoconnectomic upper bound on the variability of synaptic plasticity
Abstract
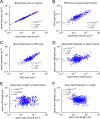
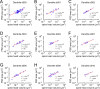
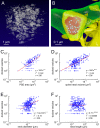
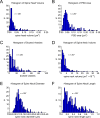
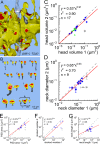
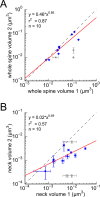
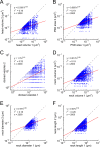
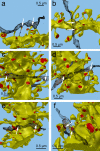
Information in a computer is quantified by the number of bits that can be stored and recovered. An important question about the brain is how much information can be stored at a synapse through synaptic plasticity, which depends on the history of probabilistic synaptic activity. The strong correlation between size and efficacy of a synapse allowed us to estimate the variability of synaptic plasticity. In an EM reconstruction of hippocampal neuropil we found single axons making two or more synaptic contacts onto the same dendrites, having shared histories of presynaptic and postsynaptic activity. The spine heads and neck diameters, but not neck lengths, of these pairs were nearly identical in size. We found that there is a minimum of 26 distinguishable synaptic strengths, corresponding to storing 4.7 bits of information at each synapse. Because of stochastic variability of synaptic activation the observed precision requires averaging activity over several minutes.
Keywords: Connectome; Neural Information Processing; Synaptic Structure and Function; neuroscience; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NS074644/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS44306/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079076/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS074644/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS21184/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH079076/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH104319/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH095980/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM103712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 NS021184/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH095980/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS044306/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS021184/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States

