HiC-Pro: an optimized and flexible pipeline for Hi-C data processing
- PMID: 26619908
- PMCID: PMC4665391
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-015-0831-x
HiC-Pro: an optimized and flexible pipeline for Hi-C data processing
Abstract
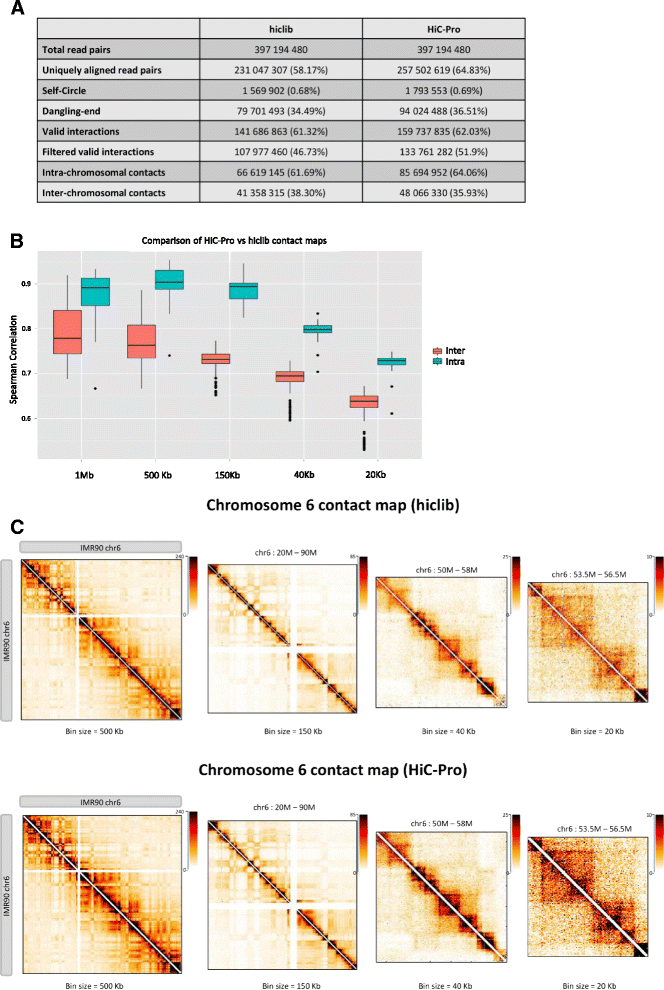
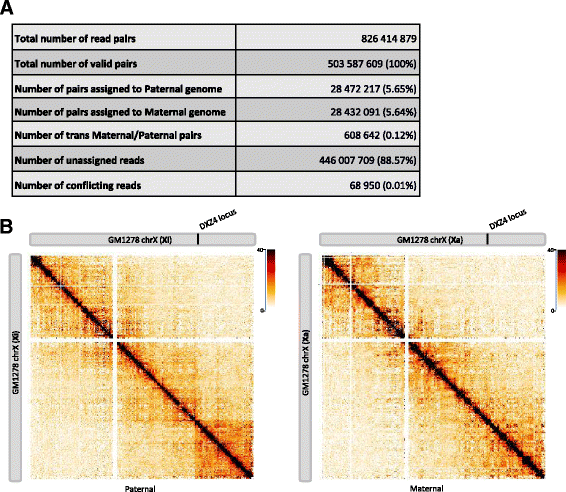
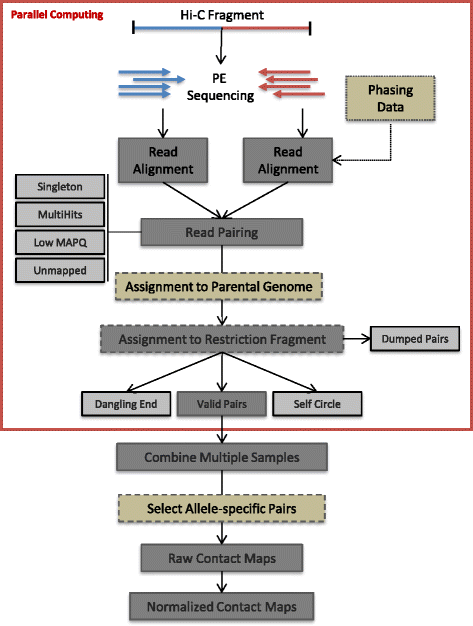
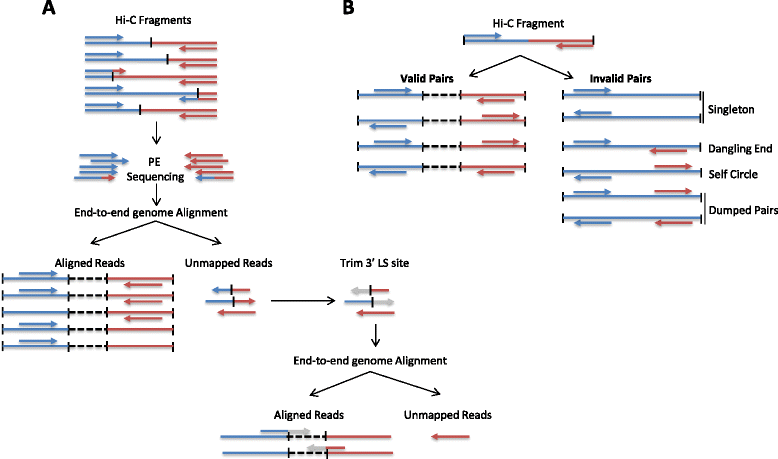
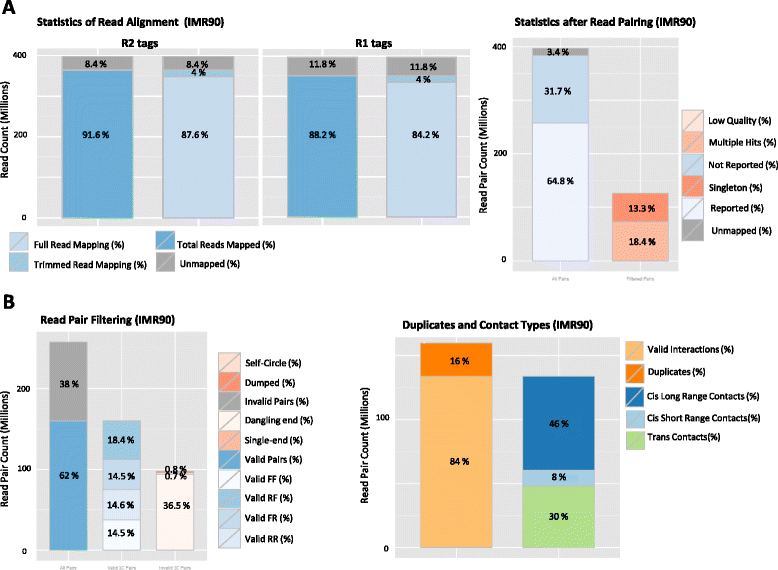
HiC-Pro is an optimized and flexible pipeline for processing Hi-C data from raw reads to normalized contact maps. HiC-Pro maps reads, detects valid ligation products, performs quality controls and generates intra- and inter-chromosomal contact maps. It includes a fast implementation of the iterative correction method and is based on a memory-efficient data format for Hi-C contact maps. In addition, HiC-Pro can use phased genotype data to build allele-specific contact maps. We applied HiC-Pro to different Hi-C datasets, demonstrating its ability to easily process large data in a reasonable time. Source code and documentation are available at http://github.com/nservant/HiC-Pro .
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

