Prediction and Characterisation of the System Effects of Aristolochic Acid: A Novel Joint Network Analysis towards Therapeutic and Toxicological Mechanisms
- PMID: 26620132
- PMCID: PMC4664954
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17646
Prediction and Characterisation of the System Effects of Aristolochic Acid: A Novel Joint Network Analysis towards Therapeutic and Toxicological Mechanisms
Abstract
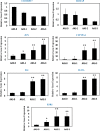
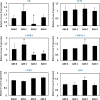
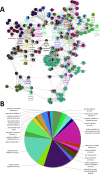
Aristolochic acid (AA) is the major active component of medicinal plants from the Aristolochiaceae family of flowering plants widely utilized for medicinal purposes. However, the molecular mechanisms of AA systems effects remain poorly understood. Here, we employed a joint network analysis that combines network pharmacology, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) database, biological processes analysis and functional annotation analysis to explore system effects. Firstly, we selected 15 protein targets (14 genes) in the PubChem database as the potential target genes and used PPI knowledge to incorporate these genes into an AA-specific gene network that contains 129 genes. Secondly, we performed biological processes analysis for these AA-related targets using ClueGO, some of new targeted genes were randomly selected and experimentally verified by employing the Quantitative Real-Time PCR assay for targeting the systems effects of AA in HK-2 cells with observed dependency of concentration. Thirdly, the pathway-based functional enrichment analysis was manipulated using WebGestalt to identify the mostly significant pathways associated with AA. At last, we built an AA target pathway network of significant pathways to predict the system effects. Taken together, this joint network analysis revealed that the systematic regulatory effects of AA on multidimensional pathways involving both therapeutic action and toxicity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Understanding the aristolochic acid toxicities in rat kidneys with regulatory networks.IET Syst Biol. 2015 Aug;9(4):141-6. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2014.0057. IET Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26243830 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated microRNA, mRNA, and protein expression profiling reveals microRNA regulatory networks in rat kidney treated with a carcinogenic dose of aristolochic acid.BMC Genomics. 2015 May 8;16(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1516-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25952319 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes aristolochic acid-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in HK-2 cells.Toxicology. 2012 Jul 16;297(1-3):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Apr 15. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22525892
-
[Aristolochic acid nephropathy].Przegl Lek. 2009;66(5):253-6. Przegl Lek. 2009. PMID: 19739583 Review. Polish.
-
[Advances in studies on pharmacokinetics of aristolochic acid I].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006 Oct;31(19):1573-5. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17165576 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Presence of Testis Determines Aristolochic Acid-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;15(2):118. doi: 10.3390/toxins15020118. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36828432 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of a chromosome-level reference genome of the ornamental butterfly Sericinus montelus based on nanopore sequencing and Hi-C analysis.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 8;14:1107353. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1107353. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36968580 Free PMC article.
-
Systems pharmacology to investigate the interaction of berberine and other drugs in treating polycystic ovary syndrome.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 16;6:28089. doi: 10.1038/srep28089. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27306862 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing a Comprehensive Picture of Biological Events From Adverse Outcome Pathways in the Drug Exposome.Front Public Health. 2021 Dec 17;9:763962. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.763962. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34976924 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of p53 on Aristolochic Acid I-Induced Gene Expression In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 6;20(24):6155. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246155. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arlt V. M., Stiborova M. & Schmeiser H. H. Aristolochic acid as a probable human cancer hazard in herbal remedies: a review. Mutagenesis 17, 265–277 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Arlt V. M. et al. Aristolochic acid mutagenesis: molecular clues to the aetiology of Balkan endemic nephropathy-associated urothelial cancer. Carcinogenesis 28, 2253–2261 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Negi P., Anandharamakrishnan C. & Jayaprakasha G. Antibacterial activity of Aristolochia bracteata root extracts. Journal of medicinal food 6, 401–403 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Cronin A. J. et al. Aristolochic acid as a causative factor in a case of Chinese herbal nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 17, 524–525 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

