High yield and ultrafast sources of electrically triggered entangled-photon pairs based on strain-tunable quantum dots
- PMID: 26621073
- PMCID: PMC4686767
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10067
High yield and ultrafast sources of electrically triggered entangled-photon pairs based on strain-tunable quantum dots
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: High yield and ultrafast sources of electrically triggered entangled-photon pairs based on strain-tunable quantum dots.Nat Commun. 2016 May 11;7:11681. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11681. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27168517 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Triggered sources of entangled photon pairs are key components in most quantum communication protocols. For practical quantum applications, electrical triggering would allow the realization of compact and deterministic sources of entangled photons. Entangled-light-emitting-diodes based on semiconductor quantum dots are among the most promising sources that can potentially address this task. However, entangled-light-emitting-diodes are plagued by a source of randomness, which results in a very low probability of finding quantum dots with sufficiently small fine structure splitting for entangled-photon generation (∼10(-2)). Here we introduce strain-tunable entangled-light-emitting-diodes that exploit piezoelectric-induced strains to tune quantum dots for entangled-photon generation. We demonstrate that up to 30% of the quantum dots in strain-tunable entangled-light-emitting-diodes emit polarization-entangled photons. An entanglement fidelity as high as 0.83 is achieved with fast temporal post selection. Driven at high speed, that is 400 MHz, strain-tunable entangled-light-emitting-diodes emerge as promising devices for high data-rate quantum applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


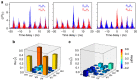
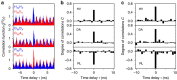
 : (b)
real part and (c) imaginary part, which are reconstructed with 16
coincidence counts integrated in a 1.8-ns temporal window centred at 0 delay
time.
: (b)
real part and (c) imaginary part, which are reconstructed with 16
coincidence counts integrated in a 1.8-ns temporal window centred at 0 delay
time.
References
-
- Knill E., Laflamme R. & Milburn G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Bouwmeester D. et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997).
-
- Gisin N. & Thew R. Quantum communication. Nat. Photon. 1, 165–171 (2007).
-
- Kwiat P. G. et al. New high-intensity source of polarization-entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4337 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Fulconis J., Alibart O., O’Brien J. L., Wadsworth W. J. & Rarity J. G. Nonclassical interference and entanglement generation using a photonic crystal fiber pair photon source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 120501 (2007). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

