Synchrotron FTIR micro-spectroscopy for structural analysis of Lewy bodies in the brain of Parkinson's disease patients
- PMID: 26621077
- PMCID: PMC4664933
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17625
Synchrotron FTIR micro-spectroscopy for structural analysis of Lewy bodies in the brain of Parkinson's disease patients
Abstract
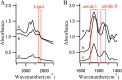
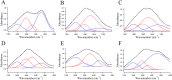
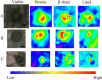
Lewy bodies (LBs), which mainly consist of α-synuclein (α-syn), are neuropathological hallmarks of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). The fine structure of LBs is unknown, and LBs cannot be made artificially. Nevertheless, many studies have described fibrillisation using recombinant α-syn purified from E. coli. An extremely fundamental problem is whether the structure of LBs is the same as that of recombinant amyloid fibrils. Thus, we used synchrotron Fourier transform infrared micro-spectroscopy (FTIRM) to analyse the fine structure of LBs in the brain of PD patients. Our results showed a shift in the infrared spectrum that indicates abundance of a β-sheet-rich structure in LBs. Also, 2D infrared mapping of LBs revealed that the content of the β-sheet structure is higher in the halo than in the core, and the core contains a large amount of proteins and lipids.
Figures


References
-
- Iwai A. et al. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 14, 467–475 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Bottner M. et al. Expression pattern and localization of alpha-synuclein in the human enteric nervous system. Neurobiol. Dis. 48, 474–480 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

