Rationale and design of A Trial of Sertraline vs. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for End-stage Renal Disease Patients with Depression (ASCEND)
- PMID: 26621218
- PMCID: PMC4818161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2015.11.020
Rationale and design of A Trial of Sertraline vs. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for End-stage Renal Disease Patients with Depression (ASCEND)
Abstract
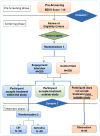
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is highly prevalent in patients with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) treated with maintenance hemodialysis (HD). Despite the high prevalence and robust data demonstrating an independent association between depression and poor clinical and patient-reported outcomes, MDD is under-treated when identified in such patients. This may in part be due to the paucity of evidence confirming the safety and efficacy of treatments for depression in this population. It is also unclear whether HD patients are interested in receiving treatment for depression. ASCEND (Clinical Trials Identifier Number NCT02358343), A Trial of Sertraline vs. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for End-stage Renal Disease Patients with Depression, was designed as a multi-center, 12-week, open-label, randomized, controlled trial of prevalent HD patients with comorbid MDD or dysthymia. It will compare (1) a single Engagement Interview vs. a control visit for the probability of initiating treatment for comorbid depression in up to 400 patients; and (2) individual chair-side CBT vs. flexible-dose treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, sertraline, for improvement of depressive symptoms in 180 of the up to 400 patients. The evolution of depressive symptoms will also be examined in a prospective longitudinal cohort of 90 HD patients who choose not to be treated for depression. We discuss the rationale and design of ASCEND, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial evaluating efficacy of non-pharmacologic vs. pharmacologic treatment of depression in HD patients for patient-centered outcomes.
Keywords: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT); Depression; End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD); Engagement interview; Hemodialysis; Sertraline.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- U.S. Renal Data System. USRDS 2012 Annual Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012.
-
- Weisbord SD, et al. Prevalence, severity, and importance of physical and emotional symptoms in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(8):2487–94. - PubMed
-
- Fukuhara S, et al. Health-related quality of life among dialysis patients on three continents: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Kidney Int. 2003;64(5):1903–10. - PubMed
-
- Mapes DL, et al. Health-related quality of life as a predictor of mortality and hospitalization: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) Kidney Int. 2003;64(1):339–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical