Severe infectious diseases of childhood as monogenic inborn errors of immunity
- PMID: 26621750
- PMCID: PMC4697435
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1521651112
Severe infectious diseases of childhood as monogenic inborn errors of immunity
Abstract
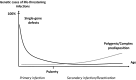
This paper reviews the developments that have occurred in the field of human genetics of infectious diseases from the second half of the 20th century onward. In particular, it stresses and explains the importance of the recently described monogenic inborn errors of immunity underlying resistance or susceptibility to specific infections. The monogenic component of the genetic theory provides a plausible explanation for the occurrence of severe infectious diseases during primary infection. Over the last 20 y, increasing numbers of life-threatening infectious diseases striking otherwise healthy children, adolescents, and even young adults have been attributed to single-gene inborn errors of immunity. These studies were inspired by seminal but neglected findings in plant and animal infections. Infectious diseases typically manifest as sporadic traits because human genotypes often display incomplete penetrance (most genetically predisposed individuals remain healthy) and variable expressivity (different infections can be allelic at the same locus). Infectious diseases of childhood, once thought to be archetypal environmental diseases, actually may be among the most genetically determined conditions of mankind. This nascent and testable notion has interesting medical and biological implications.
Keywords: human genetics; immunology; infectious diseases; pediatrics; primary immunodeficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Miller LH, Mason SJ, Clyde DF, McGinniss MH. The resistance factor to Plasmodium vivax in blacks. The Duffy-blood-group genotype, FyFy. N Engl J Med. 1976;295(6):302–304. - PubMed
-
- Miller LH, Mason SJ, Dvorak JA, McGinniss MH, Rothman IK. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975;189(4202):561–563. - PubMed
-
- Tournamille C, Colin Y, Cartron JP, Le Van Kim C. Disruption of a GATA motif in the Duffy gene promoter abolishes erythroid gene expression in Duffy-negative individuals. Nat Genet. 1995;10(2):224–228. - PubMed
-
- Samson M, et al. Resistance to HIV-1 infection in caucasian individuals bearing mutant alleles of the CCR-5 chemokine receptor gene. Nature. 1996;382(6593):722–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

