The anti-tumor NC1 domain of collagen XIX inhibits the FAK/ PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway through αvβ3 integrin interaction
- PMID: 26621838
- PMCID: PMC4811477
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6399
The anti-tumor NC1 domain of collagen XIX inhibits the FAK/ PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway through αvβ3 integrin interaction
Abstract
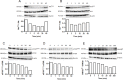
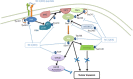
Type XIX collagen is a minor collagen associated with basement membranes. It was isolated for the first time in a human cDNA library from rhabdomyosarcoma and belongs to the FACITs family (Fibril Associated Collagens with Interrupted Triple Helices). Previously, we demonstrated that the NC1 domain of collagen XIX (NC1(XIX)) exerts anti-tumor properties on melanoma cells by inhibiting their migration and invasion. In the present work, we identified for the first time the integrin αvβ3 as a receptor of NC1(XIX). Moreover, we demonstrated that NC1(XIX) inhibits the FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, by decreasing the phosphorylation and activity of the major proteins involved in this pathway. On the other hand, NC1(XIX) induced an increase of GSK3β activity by decreasing its degree of phosphorylation. Treatments targeting this central signaling pathway in the development of melanoma are promising and new molecules should be developed. NC1(XIX) seems to have the potential for the design of new anti-cancer drugs.
Keywords: FAK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR; NC1 domain; collagen XIX; integrin; tumor invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
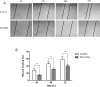
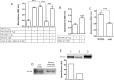

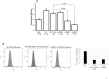
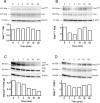
Similar articles
-
Type XIX collagen: A new partner in the interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27491275 Review.
-
Conformation-dependent binding of a Tetrastatin peptide to αvβ3 integrin decreases melanoma progression through FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 29;8(1):9837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28003-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29959360 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Adhesion- and IGF1R-Dependent Survival and Migratory Pathways Mediate Tumor Resistance to mTORC1/2 Inhibition.Mol Cell. 2017 Aug 3;67(3):512-527.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.033. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28757207 Free PMC article.
-
The NC1 domain of type XIX collagen inhibits melanoma cell migration.Eur J Dermatol. 2010 Nov-Dec;20(6):712-8. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2010.1070. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Eur J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20840910
-
Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;142(2):164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24333502 Review.
Cited by
-
TIMP1 is a prognostic marker for the progression and metastasis of colon cancer through FAK-PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 20;35(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0427-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27644693 Free PMC article.
-
Preterm birth alters the feeding-induced activation of Akt signaling in the muscle of neonatal piglets.Pediatr Res. 2023 Jun;93(7):1891-1898. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02382-4. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36402914 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Interaction of Collagen with Cell Receptors for Biological Function.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;14(5):876. doi: 10.3390/polym14050876. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multifaced Role of Collagen in Cancer Development and Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 17;25(24):13523. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413523. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor activity of integrin αVβ3 antibody conjugated-cationic microbubbles in liver cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Jun;8(3):899-908. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.05.29. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshioka H, Zhang H, Ramirez F, Mattei M-G, Moradi-Ameli M, van der Rest M, Gordon MK. Synteny between the loci for a novel FACIT-like collagen locus (D6S228E) and α1(IX) collagen (COL9A1) on 6q12–q14 in humans. Genomics. 1992;13:884–886. - PubMed
-
- Inoguchi K, Yoshioka H, Khaleduzzaman M, Ninomiya Y. The mRNA for α1(XIX) Collagen Chain, a New Member of FACITs, Contains a Long Unusual 3′ Untranslated Region and Displays Many Unique Splicing Variants. J Biochem. 1995;117:137–146. - PubMed
-
- Khaleduzzaman M, Sumiyoshi H, Ueki Y, Inoguchi K, Ninomiya Y, Yoshioka H. Structure of the human type XIX collagen (COL19A1) gene, which suggests it has arisen from an ancestor gene of the FACIT family. Genomics. 1997;45:304–312. - PubMed
-
- Myers JC, Sun MJ, D'Ippolito JA, Jabs EW, Neilson EG, Dion AS. Human cDNA clones transcribed from an unusually high-molecular-weight RNA encode a new collagen chain. Gene. 1993;123:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Myers JC, Yang H, D'Ippolito JA, Presente A, Miller MK, Dion AS. The triple-helical region of human type XIX collagen consists of multiple collagenous subdomains and exhibits limited sequence homology to alpha 1(XVI) J Biol Chem. 1994;269:18549–18557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

