ML264, A Novel Small-Molecule Compound That Potently Inhibits Growth of Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 26621868
- PMCID: PMC4707060
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0600
ML264, A Novel Small-Molecule Compound That Potently Inhibits Growth of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
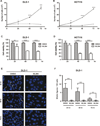
Colorectal cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer mortality in Western civilization. Studies have shown that colorectal cancer arises as a consequence of the modification of genes that regulate important cellular functions. Deregulation of the WNT and RAS/MAPK/PI3K signaling pathways has been shown to be important in the early stages of colorectal cancer development and progression. Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) is a transcription factor that is highly expressed in the proliferating intestinal crypt epithelial cells. Previously, we showed that KLF5 is a mediator of RAS/MAPK and WNT signaling pathways under homeostatic conditions and that it promotes their tumorigenic functions during the development and progression of intestinal adenomas. Recently, using an ultrahigh-throughput screening approach we identified a number of novel small molecules that have the potential to provide therapeutic benefits for colorectal cancer by targeting KLF5 expression. In the current study, we show that an improved analogue of one of these screening hits, ML264, potently inhibits proliferation of colorectal cancer cells in vitro through modifications of the cell-cycle profile. Moreover, in an established xenograft mouse model of colon cancer, we demonstrate that ML264 efficiently inhibits growth of the tumor within 5 days of treatment. We show that this effect is caused by a significant reduction in proliferation and that ML264 potently inhibits the expression of KLF5 and EGR1, a transcriptional activator of KLF5. These findings demonstrate that ML264, or an analogue, may hold a promise as a novel therapeutic agent to curb the development and progression of colorectal cancer.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Arnold CN, Goel A, Blum HE, Boland CR. Molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer: implications for molecular diagnosis. Cancer. 2005;104:2035–2047. - PubMed
-
- Fearon ER. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annual review of pathology. 2011;6:479–507. - PubMed
-
- Drost J, van Jaarsveld RH, Ponsioen B, Zimberlin C, van Boxtel R, Buijs A, et al. Sequential cancer mutations in cultured human intestinal stem cells. Nature. 2015;521:43–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

