Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 26622321
- PMCID: PMC4647139
- DOI: 10.1177/1756287215597647
Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
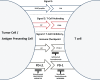
Immunostimulatory therapies have been a cornerstone of treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) since the 1990s. However, the use of traditional immunotherapeutic approaches for RCC, such as high-dose interleukin-2 and interferon-α, has been limited by significant systemic toxicities and the need to deliver these therapies at centers of expertise. Furthermore, in spite of the success of these immunostimulatory therapies for some patients with RCC, it is clear that most patients fail to respond to cytokine therapy. More effective immune therapy for RCC has therefore been necessary. The interaction between programmed death-1 (PD-1, present on T cells), and one of its ligands (PD-L1, present on antigen-presenting cells and tumor cells) constitutes an immune checkpoint through which tumors can induce T-cell tolerance and avoid immune destruction. Monoclonal antibodies that disrupt the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction serve as inhibitors of this immune checkpoint, and have demonstrated favorable activity in RCC as monotherapy and in combination with other active agents. This review summarizes the current landscape of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for RCC, and highlights challenges for the future development of this promising approach.
Keywords: PD-1; PD-L1; immunotherapy; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Amin A., Plimack E., Infante J., Ernstoff M., Rini B., McDermott D., et al. (2014) Nivolumab (anti-PD-1; BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in combination with sunitinib or pazopanib in patients (pts) with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). J Clin Oncol 32(Suppl. 15): 5010.
-
- Squibb Bristol-Myers. (2015) Checkmate -025, a pivotal phase III opdivo (nivolumab) renal cell cancer trial, stopped early. Available at: http://news.bms.com/press-release/checkmate-025-pivotal-phase-iii-opdivo... (accessed 27 July 2015).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

