Silibinin attenuates methotrexate-induced pulmonary injury by targeting oxidative stress
- PMID: 26622344
- PMCID: PMC4509095
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2015.2542
Silibinin attenuates methotrexate-induced pulmonary injury by targeting oxidative stress
Abstract
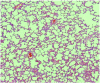
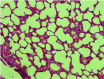
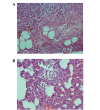
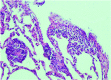
The aim of the present study was to assess the protective effect of silibinin against methotrexate (MTX)-induced pulmonary toxicity. Rats were divided into four groups (MTX, MTX + silibinin, silibinin and control. MTX was injected intraperitoneally (i.p) into female Wistar rats (10 mg/kg/day for 3 days), which resulted in significant increases in the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and oxidant enzymes, including nitric oxide and myeloperoxidase. Furthermore, significant reductions were detected in the serum activity levels of the antioxidative enzymes, glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, when compared with the control group. However, administration of silibinin (100 mg/kg/day for 10 days, i.p.) was shown to ameliorate the MTX-induced pulmonary toxicity, as indicated by the normalization of the oxidative stress parameters. Furthermore, silibinin treatment was demonstrated to reduce the histopathological changes associated with MTX. In conclusion, silibinin exhibited protective effects against MTX-induced pulmonary toxicity, which may be attributed to its antioxidant activity.
Keywords: antioxidant; methotrexate; pulmonary toxicity; rat; silibinin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of berberine against methotrexate induced liver toxicity in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:233-239. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.113. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29091871
-
Evaluation of the protective effect of silibinin against diazinon induced hepatotoxicity and free-radical damage in rat liver.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2015 Apr 25;17(4):e25310. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.17(4)2015.25310. eCollection 2015 Apr. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2015. PMID: 26023342 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of gallic acid against methotrexate-induced toxicity in rats.Acta Chir Belg. 2018 Jun;118(3):152-160. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2017.1394672. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Acta Chir Belg. 2018. PMID: 29069994
-
[Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats: Protective Effect of Mistletoe (Viscum album L.) Extract].Complement Med Res. 2017;24(6):364-370. doi: 10.1159/000468984. Epub 2017 May 4. Complement Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28467981 German.
-
Virgin coconut oil supplementation attenuates acute chemotherapy hepatotoxicity induced by anticancer drug methotrexate via inhibition of oxidative stress in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Mar;87:437-442. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.123. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28068634
Cited by
-
Nephroprotective activity of naringin against chemical-induced toxicity and renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: A review.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022 Jul-Aug;12(4):357-370. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.19620. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022. PMID: 35782769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silibinin Attenuates Silica Dioxide Nanoparticles-Induced Inflammation by Suppressing TXNIP/MAPKs/AP-1 Signaling.Cells. 2020 Mar 10;9(3):678. doi: 10.3390/cells9030678. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32164364 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydromyricetin Modulates Nrf2 and NF-κB Crosstalk to Alleviate Methotrexate-Induced Lung Toxicity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;16(4):481. doi: 10.3390/ph16040481. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111238 Free PMC article.
-
Silibinin Effect on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats.Eurasian J Med. 2022 Oct;54(3):264-269. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.20371. Eurasian J Med. 2022. PMID: 35971282 Free PMC article.
-
Silibinin inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through induction of mitochondrial fusion.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Jan;463(1-2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03640-6. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31612353
References
-
- Abelson HT, Fosburg MT, Beardsley GP, Goorin AM, Gorka C, Link M, Link D. Methotrexate-induced renal impairment: Clinical studies and rescue from systemic toxicity with high-dose leucovorin and thymidine. J Clin Oncol. 1983;1:208–216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
