ENPP1-Fc prevents mortality and vascular calcifications in rodent model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy
- PMID: 26624227
- PMCID: PMC4686714
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10006
ENPP1-Fc prevents mortality and vascular calcifications in rodent model of generalized arterial calcification of infancy
Abstract
Diseases of ectopic calcification of the vascular wall range from lethal orphan diseases such as generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI), to common diseases such as hardening of the arteries associated with aging and calciphylaxis of chronic kidney disease (CKD). GACI is a lethal orphan disease in which infants calcify the internal elastic lamina of their medium and large arteries and expire of cardiac failure as neonates, while calciphylaxis of CKD is a ubiquitous vascular calcification in patients with renal failure. Both disorders are characterized by vascular Mönckeburg's sclerosis accompanied by decreased concentrations of plasma inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). Here we demonstrate that subcutaneous administration of an ENPP1-Fc fusion protein prevents the mortality, vascular calcifications and sequela of disease in animal models of GACI, and is accompanied by a complete clinical and biomarker response. Our findings have implications for the treatment of rare and common diseases of ectopic vascular calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
R.A.A. and D.T.B. are co-inventors of a pending patent application owned by Yale University related to these studies. Z.C., K.B. and Z.-X.Y. are employees of Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
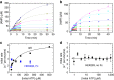

 to obtain the elimination and absorption constants ke and ka, respectively. The resulting curve yielded values for ke=0.107±0.016 h−1 and ka=0.048±0.008 h−1. The goodness of the fit yielded an R2=0.7573 and an absolute sum of squares=0.01. (c) Stability of ENPP1 therapeutic. ENPP1-Fc Ap3A activity was seen to be stable to freeze-thaw cycle in PBS following storage at −80 °C. (d) Molecular weight of ENPP1-Fc determined by SEC-MALLS/RI/UV. Weight average molar masses (Mw) are plotted for analyses of ENPP1-Fc protein at various concentrations. Lines correspond to UV traces of the protein eluting from the SEC column monitored at 280 nm (left axis). Molar masses were recorded every sec across the elution profile (circles; right axis); for clarity only every 20th measurement of molar mass is plotted. ENPP1-Fc protein was analysed in a concentration range from 100 nM (dashed line, empty circles) to 1 μM (solid line, filled circles) measured at the apex of the eluting peak. The elution's position of protein standards used for validation of SEC-MALLS/UV/RI performance are marked. The SEC-MALLS/UV/RI analysis yielded MW of 274±38 KDa with a glycosylation estimate of 0.05 g of sugars per gram of polypeptide.
to obtain the elimination and absorption constants ke and ka, respectively. The resulting curve yielded values for ke=0.107±0.016 h−1 and ka=0.048±0.008 h−1. The goodness of the fit yielded an R2=0.7573 and an absolute sum of squares=0.01. (c) Stability of ENPP1 therapeutic. ENPP1-Fc Ap3A activity was seen to be stable to freeze-thaw cycle in PBS following storage at −80 °C. (d) Molecular weight of ENPP1-Fc determined by SEC-MALLS/RI/UV. Weight average molar masses (Mw) are plotted for analyses of ENPP1-Fc protein at various concentrations. Lines correspond to UV traces of the protein eluting from the SEC column monitored at 280 nm (left axis). Molar masses were recorded every sec across the elution profile (circles; right axis); for clarity only every 20th measurement of molar mass is plotted. ENPP1-Fc protein was analysed in a concentration range from 100 nM (dashed line, empty circles) to 1 μM (solid line, filled circles) measured at the apex of the eluting peak. The elution's position of protein standards used for validation of SEC-MALLS/UV/RI performance are marked. The SEC-MALLS/UV/RI analysis yielded MW of 274±38 KDa with a glycosylation estimate of 0.05 g of sugars per gram of polypeptide.


References
-
- Moran J. J. Idiopathic arterial calcification of infancy: a clinicopathologic study. Pathol. Annu. 10, 393–417 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Otero J. E. et al.. Severe skeletal toxicity from protracted etidronate therapy for generalized arterial calcification of infancy. J. Bone Miner. Res. 28, 419–430 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Stuart A. G. Idiopathic arterial calcification of infancy and pyrophosphate deficiency. J. Pediatr. 123, 170–171 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

