Argon Mediates Anti-Apoptotic Signaling and Neuroprotection via Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 2 and 4
- PMID: 26624894
- PMCID: PMC4666627
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143887
Argon Mediates Anti-Apoptotic Signaling and Neuroprotection via Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 2 and 4
Abstract
Purpose: Recently, the noble gas argon attracted significant attention due to its neuroprotective properties. However, the underlying molecular mechanism is still poorly understood. There is growing evidence that the extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) is involved in Argon´s protective effect. We hypothesized that argon mediates its protective effects via the upstream located toll-like receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4.
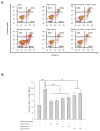
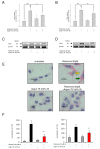
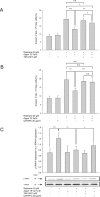
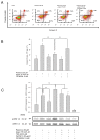
Methods: Apoptosis in a human neuroblastoma cell line (SH-SY5Y) was induced using rotenone. Argon treatment was performed after induction of apoptosis with different concentrations (25, 50 and 75 Vol% in oxygen 21 Vol%, carbon dioxide and nitrogen) for 2 or 4 hours respectively. Apoptosis was analyzed using flow cytometry (annexin-V (AV)/propidiumiodide (PI)) staining, caspase-3 activity and caspase cleavage. TLR density on the cells' surface was analyzed using FACS and immunohistochemistry. Inhibition of TLR signaling and extracellular regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) were assessed by western blot, activity assays and FACS analysis.
Results: Argon 75 Vol% treatment abolished rotenone-induced apoptosis. This effect was attenuated dose- and time-dependently. Argon treatment was accompanied with a significant reduction of TLR2 and TLR4 receptor density and protein expression. Moreover, argon mediated increase in ERK1/2 phosphorylation was attenuated after inhibition of TLR signaling. ERK1/2 and TLR signaling inhibitors abolished the anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective effects of argon. Immunohistochemistry results strengthened these findings.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that argon-mediated anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects are mediated via inhibition of TLR2 and TLR4.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367(9524):1747–57. - PubMed
-
- Langlois JA, Rutland-Brown W, Wald MM. The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview. The Journal of head trauma rehabilitation. 2006;21(5):375–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

