Neonatal near miss: a systematic review
- PMID: 26625905
- PMCID: PMC4667407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-015-0758-y
Neonatal near miss: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The concept of neonatal near miss has been proposed as a tool for assessment of quality of care in neonates who suffered any life-threatening condition. However, there are no internationally agreed concepts or criteria for defining or identifying neonatal near miss. The purpose of this study was to perform a systematic review of studies and markers that are able to identify neonatal near miss cases and predict neonatal mortality.
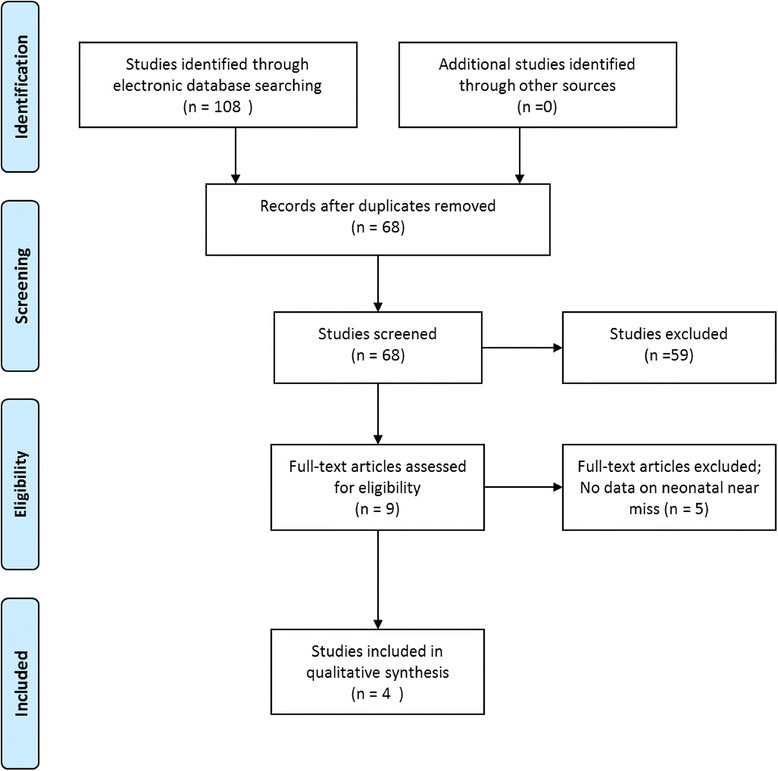
Methods: Electronic searches were performed in the Medline, Embase and Scielo databases, with no time or language restriction, until December 2014. The term "neonatal near miss" was used alone or in combination with terms related to neonatal morbidity/mortality and neonatal severity scores. Study selection criteria involved three steps: title, abstract and full text of the articles. Two researchers performed study selection and data extraction independently. Heterogeneity of study results did not permit the performance of meta-analysis.
Results: Following the inclusion and exclusion criteria adopted, only four articles were selected. Preterm and perinatal asphyxia were used as near miss markers in all studies. Health indicators on neonatal morbidity and mortality were extracted or estimated. The neonatal near miss rate was 2.6 to 8 times higher than the neonatal mortality rate.
Conclusions: Pragmatic and management criteria are used to help develop the neonatal near miss concept. The most severe cases are identified and mortality is predicted with these criteria. Furthermore, the near miss concept can be used as a tool for evaluating neonatal care. It is the first step in building management strategies to reduce mortality and long-term sequelae.
Figures
References
-
- Nations U. The millennium development goals report 2014. New York: United Nations; 2014 [http://www.undp.org/content/dam/undp/library/MDG/english/UNDP_MDGReport_... ].
-
- Unicef. Child Survival. [https://www.unicefusa.org/mission/survival]. Accessed on 24 November 2015.
-
- Unicef. Levels & Trends in Child Mortality. Report 2014. New York: United Nations Children’s Fund, 2014. [http://www.unicef.org/media/files/Levels_and_Trends_in_Child_Mortality_2...].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources