Maternal super-obesity and perinatal outcomes in Australia: a national population-based cohort study
- PMID: 26628074
- PMCID: PMC4667490
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-015-0693-y
Maternal super-obesity and perinatal outcomes in Australia: a national population-based cohort study
Abstract
Background: Super-obesity is associated with significantly elevated rates of obstetric complications, adverse perinatal outcomes and interventions. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence, risk factors, management and perinatal outcomes of super-obese women giving birth in Australia.
Methods: A national population-based cohort study. Super-obese pregnant women (body mass index (BMI) >50 kg/m(2) or weight >140 kg) who gave birth between January 1 and October 31, 2010 and a comparison cohort were identified using the Australasian Maternity Outcomes Surveillance System (AMOSS). Outcomes included maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Prevalence estimates calculated with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Adjusted odds ratios (ORs) were calculated using multivariable logistic regression.
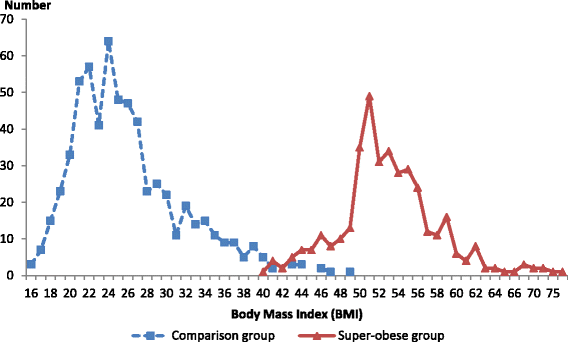
Results: 370 super-obese women with a median BMI of 52.8 kg/m(2) (range 40.9-79.9 kg/m(2)) and prevalence of 2.1 per 1 000 women giving birth (95% CI: 1.96-2.40). Super-obese women were significantly more likely to be public patients (96.2%), smoke (23.8%) and be socio-economically disadvantaged (36.2%). Compared with other women, super-obese women had a significantly higher risk for obstetric (adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 2.42, 95% CI: 1.77-3.29) and medical (AOR: 2.89, 95% CI: 2.64-4.11) complications during pregnancy, birth by caesarean section (51.6%) and admission to special care (HDU/ICU) (6.2%). The 372 babies born to 365 super-obese women with outcomes known had significantly higher rates of birthweight ≥ 4500 g (AOR 19.94, 95 % CI: 6.81-58.36), hospital transfer (AOR 3.81, 95 % CI: 1.93-7.55) and admission to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) (AOR 1.83, 95% CI: 1.27-2.65) compared to babies of the comparison group, but not prematurity (10.5% versus 9.2%) or perinatal mortality (11.0 (95% CI: 4.3-28.0) versus 6.6 (95% CI: 2.6- 16.8) per 1 000 singleton births).
Conclusions: Super-obesity in pregnancy in Australia is associated with increased rates of pregnancy and birth complications, and with social disadvantage. There is an urgent need to further address risk factors leading to super-obesity among pregnant women and for maternity services to better address pre-pregnancy and pregnancy care to reduce associated inequalities in perinatal outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- OECD. Health at a Glance 2013: OECD Indicators. Edited by EOECD. Paris, France: OECD Publishing; 2013.
-
- Hilder L, Zhichao Z, Parker M, Jahan S, Chambers G. Australia’s mothers and babies 2012. In: AIHW, editor. Perinatal statistics series no 30. Canberra: AIHW; 2014.
-
- Mason EE, Doherty C, Maher JW, Scott DH, Rodriguez EM, Blommers TJ. Super obesity and gastric reduction procedures. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 1987;16(3):495–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical