Asymmetric PI3K Signaling Driving Developmental and Regenerative Cell Fate Bifurcation
- PMID: 26628372
- PMCID: PMC4685001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.072
Asymmetric PI3K Signaling Driving Developmental and Regenerative Cell Fate Bifurcation
Abstract
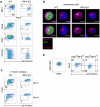
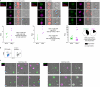
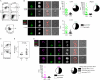
Metazoan sibling cells often diverge in activity and identity, suggesting links between growth signals and cell fate. We show that unequal transduction of nutrient-sensitive PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling during cell division bifurcates transcriptional networks and fates of kindred cells. A sibling B lymphocyte with stronger signaling, indexed by FoxO1 inactivation and IRF4 induction, undergoes PI3K-driven Pax5 repression and plasma cell determination, while its sibling with weaker PI3K activity renews a memory or germinal center B cell fate. PI3K-driven effector T cell determination silences TCF1 in one sibling cell, while its PI3K-attenuated sibling self-renews in tandem. Prior to bifurcations achieving irreversible plasma or effector cell fate determination, asymmetric signaling during initial divisions specifies a more proliferative, differentiation-prone lymphocyte in tandem with a more quiescent memory cell sibling. By triggering cell division but transmitting unequal intensity between sibling cells, nutrient-sensitive signaling may be a frequent arbiter of cell fate bifurcations during development and repair.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Basso K, Dalla-Favera R. Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nature reviews Immunology. 2015;15:172–184. - PubMed
-
- Bird JJ, Brown DR, Mullen AC, Moskowitz NH, Mahowald MA, Sider JR, Gajewski TF, Wang CR, Reiner SL. Helper T cell differentiation is controlled by the cell cycle. Immunity. 1998;9:229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

