Complete Surgical Excision Is Essential for the Management of Patients With Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 26628470
- PMCID: PMC4872006
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.3412
Complete Surgical Excision Is Essential for the Management of Patients With Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma
Erratum in
-
ERRATUM.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Mar 10;34(8):888. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.7659. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26936251 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
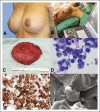
Purpose: Breast implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BI-ALCL) is a rare type of T-cell lymphoma that arises around breast implants. The optimal management of this disease has not been established. The goal of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of different therapies used in patients with BI-ALCL to determine an optimal treatment approach.
Patients and methods: In this study, we applied strict criteria to pathologic findings, assessed therapies used, and conducted a clinical follow-up of 87 patients with BI-ALCL, including 50 previously reported in the literature and 37 unreported. A Prentice, Williams, and Peterson model was used to assess the rate of events for each therapeutic intervention.
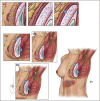
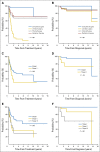
Results: The median and mean follow-up times were 45 and 30 months, respectively (range, 3 to 217 months). The median overall survival (OS) time after diagnosis of BI-ALCL was 13 years, and the OS rate was 93% and 89% at 3 and 5 years, respectively. Patients with lymphoma confined by the fibrous capsule surrounding the implant had better event-free survival (EFS) and OS than did patients with lymphoma that had spread beyond the capsule (P = .03). Patients who underwent a complete surgical excision that consisted of total capsulectomy with breast implant removal had better OS (P = .022) and EFS (P = .014) than did patients who received partial capsulectomy, systemic chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Conclusion: Surgical management with complete surgical excision is essential to achieve optimal EFS in patients with BI-ALCL.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. Author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Breast Implants. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/Implantsa...
-
- Keech JA, Jr, Creech BJ. Anaplastic T-cell lymphoma in proximity to a saline-filled breast implant. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100:554–555. - PubMed
-
- Roden AC, Macon WR, Keeney GL, et al. Seroma-associated primary anaplastic large-cell lymphoma adjacent to breast implants: An indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:455–463. - PubMed
-
- Aladily TN, Medeiros LJ, Amin MB, et al. Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma associated with breast implants: A report of 13 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:1000–1008. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) in women with breast implants: Preliminary FDA findings and analyses. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ProductsandMedicalProcedures/Implantsa....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

