An Optimal Frequency in Ca2+ Oscillations for Stomatal Closure Is an Emergent Property of Ion Transport in Guard Cells
- PMID: 26628748
- PMCID: PMC4704601
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.01607
An Optimal Frequency in Ca2+ Oscillations for Stomatal Closure Is an Emergent Property of Ion Transport in Guard Cells
Abstract
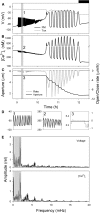
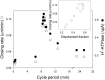
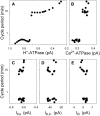
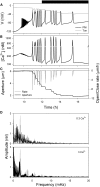
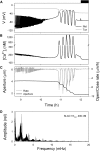
Oscillations in cytosolic-free Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i) have been proposed to encode information that controls stomatal closure. [Ca(2+)]i oscillations with a period near 10 min were previously shown to be optimal for stomatal closure in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), but the studies offered no insight into their origins or mechanisms of encoding to validate a role in signaling. We have used a proven systems modeling platform to investigate these [Ca(2+)]i oscillations and analyze their origins in guard cell homeostasis and membrane transport. The model faithfully reproduced differences in stomatal closure as a function of oscillation frequency with an optimum period near 10 min under standard conditions. Analysis showed that this optimum was one of a range of frequencies that accelerated closure, each arising from a balance of transport and the prevailing ion gradients across the plasma membrane and tonoplast. These interactions emerge from the experimentally derived kinetics encoded in the model for each of the relevant transporters, without the need of any additional signaling component. The resulting frequencies are of sufficient duration to permit substantial changes in [Ca(2+)]i and, with the accompanying oscillations in voltage, drive the K(+) and anion efflux for stomatal closure. Thus, the frequency optima arise from emergent interactions of transport across the membrane system of the guard cell. Rather than encoding information for ion flux, these oscillations are a by-product of the transport activities that determine stomatal aperture.
© 2016 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Allen GJ, Chu SP, Harrington CL, Schumacher K, Hoffmann T, Tang YY, Grill E, Schroeder JI (2001) A defined range of guard cell calcium oscillation parameters encodes stomatal movements. Nature 411: 1053–1057 - PubMed
-
- Allen GJ, Chu SP, Schumacher K, Shimazaki CT, Vafeados D, Kemper A, Hawke SD, Tallman G, Tsien RY, Harper JF, et al. (2000) Alteration of stimulus-specific guard cell calcium oscillations and stomatal closing in Arabidopsis det3 mutant. Science 289: 2338–2342 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Dupont G (1994) Spatial and temporal signalling by calcium. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6: 267–274 - PubMed
-
- Blatt MR. (2000) Cellular signaling and volume control in stomatal movements in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16: 221–241 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/F001673/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L001276/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I001187/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M001601/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L019205/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

