Role of WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 in etoposide resistance in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
- PMID: 26628978
- PMCID: PMC4658867
Role of WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 in etoposide resistance in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
Abstract
Object: The aim of this study was to explore the role of WNT1-inducible-signaling Pathway Protein 1 (WISP-1) in etoposide resistance in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.
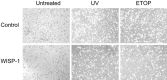
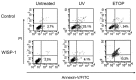
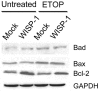
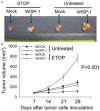
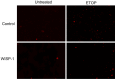
Methods: WISP-1 overexpression A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell was established. After exposure to ultraviolet (UV) and etoposide, cell viability and apoptosis were evaluated. Moreover, western-blot was employed to examine the expression of apoptotic pathway proteins. In addition, a nude mice tumor model was established to examine the effect of WISP-1 overexpression in vivo and TUNEL staining was used to assess cell apoptosis of tumor tissue.
Results: WISP-1 overexpression significantly increased cell viability and decreased cell apoptosis after treatment with UV and etoposide. Decreased expression of Bad and Bax and increased expression of Bcl-2 was found after etoposide treatment in WISP-1 overexpressed cells. A significantly increasing of tumor volume in WISP-1 overexpressed group was found and TUNEL staining revealed that decreased cell apoptosis in WISP-1 overexpressed group.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that WISP-1 may have a facilitating role in etoposide resistance through increasing cell viability and decreasing cell apoptosis.
Keywords: A549; WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1; apoptosis; etoposide; lung adenocarcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BK, Ward E, Kohler BA, Eheman C, Zauber AG, Anderson RN, Jemal A, Schymura MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Seeff LC, van Ballegooijen M, Goede SL, Ries LA. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2006, featuring colorectal cancer trends and impact of interventions (risk factors, screening, and treatment) to reduce future rates. Cancer. 2010;116:544–573. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang F, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B. Gene expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol. 2006;45:401–409. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
