Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain
- PMID: 26630545
- PMCID: PMC6483553
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006275.pub3
Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain
Update in
-
Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 14;6(6):CD006275. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006275.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37314064 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Infant acute pain and distress is commonplace. Infancy is a period of exponential development. Unrelieved pain and distress can have implications across the lifespan. This is an update of a previously published review in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 10 2011 entitled 'Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain'.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions for infant and child (up to three years) acute pain, excluding kangaroo care, and music. Analyses were run separately for infant age (preterm, neonate, older) and pain response (pain reactivity, immediate pain regulation).
Search methods: For this update, we searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library (Issue 2 of 12, 2015), MEDLINE-Ovid platform (March 2015), EMBASE-OVID platform (April 2011 to March 2015), PsycINFO-OVID platform (April 2011 to February 2015), and CINAHL-EBSCO platform (April 2011 to March 2015). We also searched reference lists and contacted researchers via electronic list-serves. New studies were incorporated into the review. We refined search strategies with a Cochrane-affiliated librarian. For this update, nine articles from the original 2011 review pertaining to Kangaroo Care were excluded, but 21 additional studies were added.
Selection criteria: Participants included infants from birth to three years. Only randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or RCT cross-overs that had a no-treatment control comparison were eligible for inclusion in the analyses. However, when the additive effects of a non-pharmacological intervention could be assessed, these studies were also included. We examined studies that met all inclusion criteria except for study design (e.g. had an active control) to qualitatively contextualize results. There were 63 included articles in the current update.
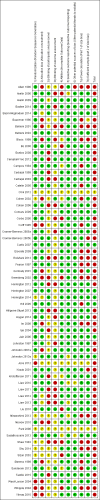
Data collection and analysis: Study quality ratings and risk of bias were based on the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool and GRADE approach. We analysed the standardized mean difference (SMD) using the generic inverse variance method.
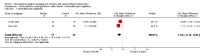
Main results: Sixty-three studies, with 4905 participants, were analysed. The most commonly studied acute procedures were heel-sticks (32 studies) and needles (17 studies). The largest SMD for treatment improvement over control conditions on pain reactivity were: non-nutritive sucking-related interventions (neonate: SMD -1.20, 95% CI -2.01 to -0.38) and swaddling/facilitated tucking (preterm: SMD -0.89; 95% CI -1.37 to -0.40). For immediate pain regulation, the largest SMDs were: non-nutritive sucking-related interventions (preterm: SMD -0.43; 95% CI -0.63 to -0.23; neonate: SMD -0.90; 95% CI -1.54 to -0.25; older infant: SMD -1.34; 95% CI -2.14 to -0.54), swaddling/facilitated tucking (preterm: SMD -0.71; 95% CI -1.00 to -0.43), and rocking/holding (neonate: SMD -0.75; 95% CI -1.20 to -0.30). Fifty two of our 63 trials did not report adverse events. The presence of significant heterogeneity limited our confidence in the findings for certain analyses, as did the preponderance of very low quality evidence.
Authors' conclusions: There is evidence that different non-pharmacological interventions can be used with preterms, neonates, and older infants to significantly manage pain behaviors associated with acutely painful procedures. The most established evidence was for non-nutritive sucking, swaddling/facilitated tucking, and rocking/holding. All analyses reflected that more research is needed to bolster our confidence in the direction of the findings. There are significant gaps in the existing literature on non-pharmacological management of acute pain in infancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Rebecca Pillai Riddell C.Psych.: No conflict to declare.
Nicole Racine, M.A.: No conflict to declare
Hannah Gennis, B.A.: No conflict to declare
Kara Turcotte, M.A.: No conflict to declare.
Dr. Lindsay Uman, R.Psych: No conflict to declare.
Dr. Rachel Horton, C.Psych (supervised practice): No conflict to declare.
Dr. Sara Ahola Kohut, C.Psych: No conflict to declare.
Jessica Hillgrove‐Stuart, M.A.: No conflict to declare.
Dr. Bonnie Stevens, RN, PhD: No conflict to declare.
Diana Lisi, B.A.: No conflict to declare.
Figures








Update of
-
Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;(10):CD006275. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006275.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 02;(12):CD006275. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006275.pub3. PMID: 21975752 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Allen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Allen KD, White DD, Walburn JN. Sucrose as an analgesic agent for infants during immunization injections. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 1996;150(3):270‐4. - PubMed
Axelin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Axelin A, Salantera S, Lehtonen L. Facilitated tucking by parents in pain management of preterm infants ‐ a randomized crossover trial. Early Human Development 2006;82:241‐7. - PubMed
Axelin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Axelin A, Salantera S, Kirjavainen J, Lehtonen L. Oral glucose and parental holding preferable to opioid in pain management in preterm infants. Clinical Journal of Pain 2009;25:138‐45. - PubMed
Badiee 2014 {published data only}
-
- Badiee Z, Nassir Z, Armanian A. Cobedding of twin premature infants: calming effects on pain responses. Pediatrics and Neonatology 2014;55(4):262‐268. - PubMed
Basiri‐Moghadam 2014 {published data only}
-
- Basiri‐Moghadam M, Kianmehr M, Pasban‐Noghabi S, Basiri‐Moghadam K. Comparison of EMLA cream with rattles on reducing immunization pain in four month infants. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2014;64(8):874‐878. - PubMed
Bauchner 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bauchner H, Vinci R, Bak S, Pearson C, Corwin MJ. Parents and procedures: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 1996;98(5):861‐7. - PubMed
Bellieni 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bellieni CV, Buonocore G, Nenci A, Franci N, Cordelli DM, Bagnoli F. Sensorial saturation: an effective analgesic tool for heel‐prick in preterm infants. Biology of the Neonate 2001;80(1):15‐8. - PubMed
Bellieni 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bellieni CV, Bagnoli F, Perrone S, Nenci A, Cordelli DM, Fusi M, et al. Effect of multisensory stimulation on analgesia in term neonates: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Research 2002;51(4):460‐3. - PubMed
Blass 1999 {published data only}
-
- Blass EM, Watt LB. Suckling‐ and sucrose‐induced analgesia in human newborns. Pain 1999;83(3):611‐23. - PubMed
Bo 2000 {published data only}
Bustos 2008 {published data only}
Campbell‐Yeo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Campbell‐Yeo ML, Johnston CC, Joseph KS, Feely N, Chambers CT, Barrington KJ. Cobedding and recovery time after heel lance in preterm twins: results of a randomized trial. Pediatrics September 2012;130:500‐6. - PubMed
Campos 1994 {published data only}
-
- Campos RG. Rocking and pacifiers: two comforting interventions for heelstick pain. Research in Nursing & Health 1994;17(5):321‐31. - PubMed
Carbajal 1999 {published data only}
Carbajal 2003 {published data only}
Catelin 2005 {published data only}
Chik 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chik Y, Ip W. The effect of limb massage on infant's venipuncture pain. Journal of Pain 2012;13:S89. - PubMed
Cohen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cohen LL. Reducing infant immunization distress through distraction. Health Psychology 2002;21(2):207‐11. - PubMed
Cohen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cohen LL, MacLaren JE, Fortson BL, Friedman A, DeMore M, Lim CS, et al. Randomized clinical trial of distraction for infant immunization pain. Pain 2006;125(1‐2):165‐71. - PubMed
Comaru 2009 {published data only}
Corbo 2000 {published data only}
-
- Corbo MG, Mansi G, Stagni A, Romano A, Heuvel J, Capasso L et al. Nonnutritive sucking during heelstick procedures decreases behavioral distress in the newborn infant. Biology of the Neonate 2000;77(3):162‐7. - PubMed
Corff 1995 {published data only}
-
- Corff KE, Seideman R, Venkataraman PS, Lutes L, Yates B. Facilitated tucking: a nonpharmacologic comfort measure for pain in preterm neonates. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing 1995;24(2):143‐7. - PubMed
Cramer‐Berness 2005a {published data only}
-
- Cramer‐Berness LJ, Friedman AG. Behavioral interventions for infant immunizations. Children's Health Care 2005;34(2):95‐111.
Cramer‐Berness 2005b {published data only}
-
- Cramer‐Berness LJ. A comparison of behavioral interventions for infant immunizations. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2005;66(12‐B):6916.
Curtis 2007 {published data only}
Elserafy 2009 {published data only}
Esfahani 2013 {published data only}
-
- Esfahani MS, Sheykhi S, Abdeyazdan Z, Jodakee M, Boroumandfar K. A comparative study on vaccination pain in the methods of massage therapy and mothers’ breast feeding during injection of infants referring to Navabsafavi Health Care Center in Isfahan. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research 2013;18(6):494‐498. - PMC - PubMed
Fearon 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fearon I, Kisilevsky BS, Hains SMJ, Muir DW, Tranmer J. Swaddling after heel lance: age‐specific effects on behavioral recovery in preterm infants. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1997;18(4):222‐32. - PubMed
Gormally 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gormally S, Barr RG, Wertheim L, Alkawaf R, Calinoiu N, Young SN. Contact and nutrient caregiving effects on newborn infant pain responses. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2001;43(1):28‐38. - PubMed
Greenberg 2002 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg CS. A sugar‐coated pacifier reduces procedural pain in newborns. Pediatric Nursing 2002;28(3):271‐7. - PubMed
Harrington 2012 {published data only}
-
- Harrington JW, Logan S, Harwell C, Gardner J, Swingle J, McGuire E, et al. Efffective analgesia using physical interventions for infant immunizations. Pediatrics 2012;129(5):815‐22. - PubMed
Herrington 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Herrington CJ. Reducing pain of heelstick in premature infants with gentle human touch. Wayne State University Doctoral Dissertation unpublished:1‐229.
Herrington 2014 {published data only}
-
- Herrington CJ, Chiodo LM. Human touch effectively and safely reduces pain in the newborn intensive care unit. Pain Management Nursing 2014;15(1):107‐115. - PubMed
Hill 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hill S, Engle S, Jorgensen J, Kralik A, Whitman K. Effects of facilitated tucking during routine care of infants born preterm. Pediatric Physical Therapy 2005;17(2):158‐63. - PubMed
Hillgrove Stuart 2013 {published data only}
Hogan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hogan ME, Probst J, Wong K, Pillai Riddell R, Katz J, Taddio A. A randomized‐controlled trial of parent‐led tactile stimulation to reduce pain during infant immunization injections. Clinical Journal of Pain 2014;30(3):259‐265. - PubMed
Im 2008 {published data only}
-
- Im H, Kim E, Park E, Sung K, Oh W. Pain reduction of heel stick in neonates: Yakson compared to non‐nutritive sucking. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2008;54(1):31‐5. - PubMed
Ipp 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ipp M, Taddio A, Goldbach M, Ben David S, Stevens B, Koren G. Effects of age, gender and holding on pain response during infant immunization. Canadian Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2004;11(1):e2‐7. - PubMed
Jain 2006 {published data only}
Johnston 1997 {published data only}
-
- Johnston CC, Stremler RL, Stevens BJ, Horton LJ. Effectiveness of oral sucrose and simulated rocking on pain response in preterm neonates. Pain 1997;72(1‐2):193‐9. - PubMed
Johnston 2007a {published data only}
-
- Johnston CC, Filion F, Nuyt AM. Recorded maternal voice for preterm neonates undergoing heel lance. Advances in Neonatal Care 2007;7(5):258‐66. - PubMed
Johnston 2013a {published data only}
-
- Johnston C, Campbell‐Yeo M, Rich B, Whitley J, Filion F, Cogan J, et al. Therapeutic touch is not therapeutic for procedural pain in very preterm neonates. Clinical Journal of Pain 2013;29(9):824‐29. - PubMed
Jose 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jose RM, Soluchana B, Shetty S. Effectiveness of skin tap technique in reducing pain response. International Journal of Nursing Education 2012;4(1):56‐7.
Kozub 2001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kozub ML. The effect of therapeutic touch on pain response in infants receiving injections. Ohio: Medical College of Ohio, 2001.
Kristoffersen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kristoffersen L, Skogvoll E, Hafstrom M. Pain reduction in insertion of a feeding tube in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 2011;127(6):1449‐54. - PubMed
Liaw 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liaw J, Yang L, Ti Y, Tucker Blackburn S, Chang Y, Sun L. Non‐nutritive sucking relieves pain for preterm infants during heel stick procedures in Taiwan. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;19:2741‐51. - PubMed
Liaw 2011 {published data only}
-
- Liaw JJ, Zeng WP, Yang L, Yuh YS, Yin T, Yang MH. Nonnutritive sucking and oral sucrose relieve neonatal pain during intramuscular injection of hepatitis vaccine. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2011;42(6):918‐29. - PubMed
Liaw 2012 {published data only}
-
- Liaw JJ, Yang L, Wang KWK, Chen CM, Chang YC, Yin T. Non‐nutritive sucking and facilitated tucking relieve preterm infant pain during heel‐stick procedures: a prospective, randomised controlled crossover trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2012;49:300‐9. - PubMed
Liaw 2013 {published data only}
-
- Liaw JJ, Yang L, Lee CM, Fan HC, Chang YC, Cheng, LP. Effects of combined use of non‐nutritive sucking, oral sucrose, and facilitated tucking on infant behavioural states across heel‐stick procedures: a prospective, randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2013;50:883‐94. - PubMed
Liu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liu M, Lin K, Chou Y, Lee T. Using non‐nutritive sucking and oral glucose solution with neonates to relieve pain: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;19:1604‐11. - PubMed
Mirzarahimi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mirzarahimi M, Mehrnoush N, Shahizadeh S, Samadi N, Amani F. Effect of non‐nutritive sucking and leg massage on physiological and behavioural indicators of pain following heel blood sampling in term neonates. International Journal of Advanced Nursing Studies 2013;2(2):74‐79.
Morrow 2010 {published data only}
-
- Morrow C, Hidinger A, Wilkinson‐Faulk D. Reducing neonatal pain during routine heel lance procedures. American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing 2010;35(6):346‐54. - PubMed
Park 2006 {published data only}
-
- Park ES, Sung KS, Oh WO, Im HS, Kim ES, Kim YA, et al. Pain relieving effect of yakson therapy for infants. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi 2006;36(6):10. - PubMed
Sadathosseini 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sadathosseini AS, Negarandeb R, Movahedi Z. The effect of a familiar scent on the behavioural and physiological pain responses in neonates. Pain Management Nursing 2013;14(4):e196‐203. - PubMed
Shaw 1982 {published data only}
-
- Shaw EG, Routh DK. Effect of mother presence on children's reaction to aversive procedures. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1982;7(1):33‐42. - PubMed
Shu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shu SH, Lee YL, Hayter M, Wang RH. Efficacy of swaddling and heel warming on pain response to heel stick in neonates: a randomised control trial. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2014;23(21‐22):3107‐3114. - PubMed
Sizun 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sizun J, Ansquer H, Browne J, Tordjman S, Morin JF. Developmental care decreases physiologic and behavioral pain expression in preterm neonates. Journal of Pain 2002;3(6):446‐50. - PubMed
Stevens 1999 {published data only}
-
- Stevens B, Johnston C, Franck L, Petryshen P, Jack A, Foster G. The efficacy of developmentally sensitive interventions and sucrose for relieving procedural pain in very low birth weight neonates. Nursing Research 1999;48(1):35‐43. - PubMed
Sundaram 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sundaram B, Shrivastava S, Pandian JP, Singh VP. Facilitated tucking on pain in pre‐term newborns during neonatal intensive care: a single blinded randomized controlled cross‐over pilot trial. Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine 2013;6(1):19‐27. - PubMed
Taddio 2015 {published data only}
-
- Taddio A, Parikh C, Yoon EW, Sgro M, Singh H, Habtom E, et al. Impact of parent‐directed education on parental use of pain treatments during routine infant vaccination: a cluster randomized trial. Pain 2015;156(1):185‐191. - PubMed
Ward‐Larson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ward‐Larson C, Horn RA, Gosnell F. The efficacy of facilitated tucking for relieving procedural pain of endotracheal suctioning in very low birthweight infants. MCN: The American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing 2004;29(3):151‐6. - PubMed
Whipple 2004 {published data only}
-
- Whipple J. The effect of music‐reinforced nonnutritive sucking on state of preterm, low birthweight infants experiencing heelstick. Florida: The Florida State University, 2004. - PubMed
Yilmaz 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yilmaz F, Arikan D. The effects of various interventions to newborns on pain and duration of crying. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;20:1008‐17. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdallah 2013 {published data only}
-
- Abdallah B, Badr LK, Hawwari, M. The efficacy of massage on short and long term outcomes in preterm infants. Infant Behavior and Development 2013;36:662‐669. - PubMed
Abedin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Abedin S, Kapoor G. Peripherally inserted central venous catheters are a good option for prolonged venous access in children with cancer. Pediatric Blood Cancer 2008;51:251‐5. - PubMed
Aguirre 2008 {published data only}
-
- Aguirre Unceta‐Barrenechea A, Saitua Iturriaga G, Sainz de Rozas Aparicio I, Riveira Fernandez D. Analgesia when taking heel‐lance blood in the newborn. Anales de Pediatria 2008;69(6):544‐7. - PubMed
Akcan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Akcan E, Yigit R, Atici A. The effect of kangaroo care on pain in premature infants during invasive procedures. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2009;51:14‐8. - PubMed
Al‐Bekaa 2003 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Bekaa S. Harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy vs diathermy tonsillectomy: a comparative study. Australian Journal of Otolaryngology 2003;6(2):78‐80.
Aslanabadi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Aslanabadi S, Ghalehgolab‐Behbahan A, Zarrintan S, Jamshidi M, Seyyedhejazi M. Transanal one‐stage endorectal pull‐through for Hirschsprung's disease: a comparison with the staged procedures. Pediatric Surgery International 2008;24:925‐9. - PubMed
Axelin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Axelin A, Lehtonen L, Pelander T, Slantera S. Mothers' different styles of involvement in preterm infant pain care. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 2010;39:415‐24. - PubMed
Badiee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Badiee Z, Asghari M, Mohammadizadeh M. The calming effect of maternal breast milk odor on premature infants. Pediatrics and Neonatology 2013;54:322‐325. - PubMed
Bellieni 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bellieni CV, Bagnoli F, Cordelli DM, Perrone S, Nenci A, Buonocore G. Analgesia for premature children. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 2003;29(4):286‐90.
Bellieni 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bellieni CV, Cordelli DM, Marchi S, Ceccarelli S, Perrone S, Maffei M, et al. Sensorial saturation for neonatal analgesia. Clinical Journal of Pain 2007;23(3):219‐21. - PubMed
Boots 2010 {published data only}
-
- Boots BK, Edmundson EE. A controlled, randomised trial comparing single to multiple application lidocaine analgesia in paediatric patients undergoing urethral catheterisation procedures. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;19:744‐8. - PubMed
Bueno 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bueno M, Bussotti E, DaSilva A, Leao E. Non nutritive sucking and swaddling for pain relief in term neonates. Abstract from the International Symposium on Pediatric Pain 2010:1.
Campbell‐Yeo 2009 {published data only}
Campos 1989 {published data only}
-
- Campos RG. Soothing pain‐elicited distress in infants with swaddling and pacifiers. Child Development 1989;60(4):781‐92. - PubMed
Carlson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Carlson KL, Broome M, Vessey JA. Using distraction to reduce reported pain, fear, and behavioral distress in children and adolescents: a multisite study. Journal of the Society of Pediatric Nurses 2000;5(2):75‐85. - PubMed
Castral 2008 {published data only}
-
- Castral TC, Warnock F, Leite AM, Haas VJ, Scochi, CGS. The effects of skin‐to‐skin contact during acute pain in preterm newborns. European Journal of Pain 2008;12:464‐471. - PubMed
Chermont 2009 {published data only}
Cignacco 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cignacco E, Hamers JP, Lingen RA, Zimmermann LJI, Muller R, Gessler P, et al. Pain relief in ventilated preterm infants during endotracheal suctioning: a randomized controlled trial. Swiss Medical Weekly 2008;138(43‐44):635‐45. - PubMed
Cologna 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cologna M, Sperandio L. The effect of two different methods of heel lancing on pain reaction in preterm neonates. Assistenza Infermieristica e Ricerca:Air 1999;18(4):185‐92. - PubMed
Cong 2009 {published data only}
D'Agostino 2008 {published data only}
-
- D'Agostino R, Tarantino V, Calevo MG. Blunt dissection versus electronic molecular resonance bipolar dissection for tonsillectomy: operative time and intraoperative and postoperative bleeding and pain. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 2008;72(7):1077‐84. - PubMed
Dahlquist 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dahlquist LM, Pendley JS, Landthrip DS, Jones CL, Steuber CP. Distraction intervention for preschoolers undergoing intramuscular injections and subcutaneous port access. Health Psychology 2002;21(1):94‐9. - PubMed
De Jong 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jong M, Lucas C, Bredero H, Adrichem L, Ribboel D, Dijk M. Does postoperative 'M' technique massage with or without mandarin oil reduce infants' distress after major craniofacial surgery?. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2012;68(8):1748‐57. - PubMed
de Sousa 2008 {published data only}
Diego 2009 {published data only}
Dilen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dilen B, Elseviers M. Oral glucose solution as pain relief in newborns: results of a clinical trial. Birth: Issues in Perinatal Care 2010;37(2):98‐105. - PubMed
Downey 2012 {published data only}
-
- Downey LV, Zun S. The impact of watching cartoons for distraction during painful procedures in the emergency department. Pediatric Emergency Care 2012;28(10):1033‐35. - PubMed
Drago 2009 {published data only}
Duncan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Duncan B, Barton L, Edmonds D, Blashill BM. Parental perceptions of the therapeutic effect from osteopathic manipulation or acupuncture in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Clinical Pediatrics 2004;43(4):349‐53. - PubMed
El‐Naggar 2010 {published data only}
-
- El‐Naggar W, Yiu A, Mohamed A, Shah V, Manley J, McNamara P, et al. Comparison of pain during two methods of urine collection in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2010;125(6):1224‐9. - PubMed
Favara‐Scacco 2001 {published data only}
-
- Favara‐Scacco C, Smirne G, Schiliro G, Cataldo A. Art therapy as support for children with leukemia during painful procedures. Medical & Pediatric Oncology 2001;36(4):474‐80. - PubMed
Felt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Felt BT, Mollen E, Diaz S, Renaud E, Zeglis M, Wheatcroft G, et al. Behavioral interventions reduce infant distress at immunization. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medine 2000;154:719‐724. - PubMed
Ferber 2008 {published data only}
Gedaly‐Duff 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gedaly‐Duff V, Burns C. Reducing children's pain‐distress associated with injections using cold: a pilot study. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners 1992;4(3):95‐9. - PubMed
Gold 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gold JI, Kim SH, Kant AJ, Joseph MH, Rizzo AS. Effectiveness of virtual reality for pediatric pain distraction during i.v. placement. Cyberpsychology & Behavior 2006;9(2):207‐12. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1989 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez JC, Routh DK, Saab PG, Armstrong FD, Shifman L, Guerra E et al. Effects of parent presence on children's reactions to injections: behavioral, physiological, and subjective aspects. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1989;14(3):449‐62. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez JC, Routh DK, Armstrong FD. Effects of maternal distraction versus reassurance on children's reactions to injections. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1993;18(5):593‐604. - PubMed
Goubet 2003 {published data only}
-
- Goubet N, Rattaz C, Pierrat V, Bullinger A, Lequien P. Olfactory experience mediates response to pain in preterm newborns. Developmental Psychobiology 2003;42(2):171‐80. - PubMed
Goubet 2007 {published data only}
-
- Goubet N, Strasbaugh K, Chesney J. Familiarity breeds content? Soothing effect of a familiar odor on full‐term newborns. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 2007;28(3):189‐94. - PubMed
Gray 2000 {published data only}
-
- Gray L, Watt L, Blass EM. Skin‐to‐skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 2000;105(1):e14. - PubMed
Greenberg 1997 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg CS. An evaluation of the efficacy of selected nonpharmacologic pain interventions in infants. San Diego: University of San Diego, 1997.
Grunau 2004 {published data only}
Ha 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ha YO, Kim HS. The effects of audiovisual distraction on children's pain during laceration repair. International Journal of Nursing Practice 2013;19(3):20‐27. - PubMed
Hanson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hanson D, Hall W, Mills LL, Au S, Bhagat R, Hernandez M, et al. Comparison of distress and pain in infants randomized to groups receiving standard versus multiple immunizations. Infant Behavior and Development 2010;33:289‐96. - PubMed
Harrison 2000 {published data only}
-
- Harrison LL, Williams AK, Berbaum ML, Stem JT, Leeper J. Physiologic and behavioral effects of gentle human touch on preterm infants. Research in Nursing & Health 2000;23(6):435‐46. - PubMed
Hatem 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hatem TP, Lira PI, Mattos SS. The therapeutic effects of music in children following cardiac surgery. Jornal de Pediatria 2006;82(3):186‐92. - PubMed
He 2010 {published data only}
-
- He H, Jahja R, Lee T, Ang E, Sinnappan R, Vehvilainen‐Julkunen K, et al. Nurses' use of non‐pharmacological methods in children's postoperative pain management: educational intervention study. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2010;66(11):2398‐409. - PubMed
Heden 2009 {published data only}
Hoffman 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hoffman HG, Richards TL, Bills AR, Oostrom T, Magula J, Seibel EJ, et al. Using fMRI to study the neural correlates of virtual reality analgesia. CNS Spectrums 2006;11(1):45‐51. - PubMed
Holsti 2005 {published data only}
-
- Holsti L, Grunau RE, Oberlander TF, Whitfield MF. Prior pain induces heightened motor responses during clustered care in preterm infants in the NICU. Early Human Development 2005;81(3):293‐302. - PubMed
Hsu 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hsu CY, Huang LM, Lee CY, Lin TY, Lee PI, Chen JM. Local massage after vaccination enhances the immunogenicity of diphtheria‐ tetanus‐pertussis vaccine. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1995;14(7):567‐72. - PubMed
Huang 1999 {published data only}
-
- Huang FY, Huang LM. Effect of local massage on vaccination: DTP and DTPa. Acta Paediatrica Taiwanica 1999;40(3):166‐70. - PubMed
Huang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Huang CM, Tung WS, Kuo LL, Ying‐Ju C. Comparison of pain responses of premature infants to the heelstick between containment and swaddling. Journal of Nursing Research 2004;12(1):31‐40. - PubMed
Ida 2008 {published data only}
Ipp 2007 {published data only}
Ipp 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ipp M, Parkin PC, Lear N, Goldbach M, Taddio A. Order of vaccine injection and infant pain response. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2009;163(5):469‐72. - PubMed
Jackson 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jackson LA, Starkovich P, Dunstan M, Yu O, Nelson J, Dunn J, et al. Prospective assessment of the effect of needle length and injection site on the risk of local reactions to the fifth diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis vaccination. Pediatrics 2008;21(3):e646‐52. - PubMed
Jo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jo SH, Mathiasen RA, Gurushanthaiah D. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial of a hemostatic sealant in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Otolaryngology ‐ Head & Neck Surgery 2007;137(3):154‐8. - PubMed
Johnston 2003 {published data only}
-
- Johnston CC, Stevens B, Pinelli J, Gibbins S, Filion F, Jack A, et al. Kangaroo care is effective in diminishing pain response in preterm neonates. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(11):1084‐8. - PubMed
Johnston 2007b {published data only}
-
- Johnston CC, Gagnon A, Rennick J, Rosmus C, Patenaude H, Ellis J, et al. One‐on‐one coaching to improve pain assessment and management practices of pediatric nurses. Pediatric Nursing 2007;22(6):467‐78. - PubMed
Johnston 2008a {published data only}
Johnston 2009 {published data only}
Kashaninia 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kashaninia Z, Sajedi F, Rahgozar M, Noghabi FA. The effect of kangaroo care on behavioral responses to pain of an intramuscular injection in neonates. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing 2008;13(4):275‐80. - PubMed
Kivijärvi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kivijärvi R, Palviainen J. "Just like I had kicked my toe" ‐‐ Children's experiences of postsurgical pain. Sairaanhoitaja 2008;81(1):27‐9.
Koivusalo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Koivusalo AI, Korpela R, Wirtavuori K, Piiparinen S, Rintala RJ, Pakarinen MP. A single‐blinded, randomized comparison of laparoscopic versus open hernia repair in children. Pediatrics 2009;123(1):332‐7. - PubMed
Kostandy 2008 {published data only}
Leclair 2007 {published data only}
-
- Leclair MD, Plattner V, Mirallie E, Lejus C, Nguyen JM, Podevin G, et al. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2007;42(4):692‐8. - PubMed
Li 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li HCW, Lopez V, Lee TLI. Effects of preoperative therapeutic play on outcomes of school‐age children undergoing day surgery. Research in Nursing & Health 2007;30(3):320‐32. - PubMed
Lima 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lima AH, Hermont AP, Lima Friche AA. Analgesia in newborns: a case‐control study of the efficacy of nutritive and non‐nutritive sucking stimuli. CoDAS 2013;25(4):365‐368. - PubMed
Ludington‐Hoe 2005 {published data only}
Luthy 2013 {published data only}
-
- Luthy KE, Beckstand RL, Pulsipher A. Evaluation of methods to relieve parental perceptions of vaccine‐associated pain and anxiety in children: a pilot study. Journal of Pediatric Health Care 2013;27(5):351‐58. - PubMed
MacLaren 2005 {published data only}
-
- MacLaren JE, Cohen LL. A comparison of distraction strategies for venipuncture distress in children. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2005;30(5):387‐96. - PubMed
Manne 1990 {published data only}
-
- Manne SL, Redd WH, Jacobsen PB, Gorfinkle K, Schorr O, Rapkin B. Behavioral intervention to reduce child and parent distress during venipuncture. Journal of Consulting & Clinical Psychology 1990;58(5):565‐72. - PubMed
Marchisotti 2007 {published data only}
-
- Marchisotti FG, Carvalho LR, Berger K, Arnhold IJ, Mendonca BB. Growth hormone (GH) deficiency treatment in children: comparison between uses of pen versus bottles/syringes on GH administration. Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia 2007;51(7):1093‐6. - PubMed
Marec‐Berard 2009 {published data only}
Marin Gabriel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Marin Gabriel MA, Llana Martin I, Lopez Escobar A, Fernandez Villalba E, Romero Blanco I, Touza Pol P. Randomized controlled trial of early skin‐to‐skin contact: effects on the mother and the newborn. Acta Paediatrica 2010;99:1630‐4. - PubMed
McCarthy 2010 {published data only}
Mercer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mercer M, Whittle E, Nelson L, Ingram C, O'Hare A. Developmental delay confers increased distress prior to first venepuncture: Findings from an RCT of distress‐reducing interventions employing 'Social Stories'. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology (Poster Session 1) 2013:55.
Michel 2008 {published data only}
-
- Michel RG, Weinstock BI, Tsau K. Safety and efficacy of pressure‐assisted tissue‐welding tonsillectomy: a preliminary evaluation. Ear, Nose & Throat Journal 2008;87(2):100‐12. - PubMed
Morelius 2009 {published data only}
-
- Morelius E, Theodorsson E, Nelson N. Stress at three‐month immunization: parents' and infants' salivary cortisol response in relation to the use of pacifier and oral glucose. European Journal of Pain 2009;13(2):202‐8. - PubMed
Mucignat 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mucignat V, Ducrocq S, Lebas F, Mochel F, Baudon JJ, Gold F. Analgesic effects of Emla cream and saccharose solution for subcutaneous injections in preterm newborns: a prospective study of 265 injections. Archives de Pediatrie 2004;11(8):921‐5. - PubMed
Okan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Okan F, Ozdil A, Bulbul A, Yapici Z, Nuhoglu A. Analgesic effects of skin‐to‐skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2010;30:119‐28. - PubMed
Ozdogan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ozdogan T, Akman I, Cebeci D, Bilgen H, Ozek E. Comparison of two doses of breast milk and sucrose during neonatal heel prick. Pediatrics International 2010;52:175‐9. - PubMed
Phipps 2005 {published data only}
-
- Phipps S, Dunavant M, Gray E, Rai SN. Massage therapy in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: results of a pilot trial. Journal of Cancer Integrative Medicine 2005;3(2):62‐70.
Rattaz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rattaz C, Goubet N, Bullinger A. The calming effect of a familiar odor on full‐term newborns. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 2005;26(2):86‐92. - PubMed
Reichel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Reichel O, Mayr D, Winterhoff J, Chaux R, Hagedorn H, Berghaus A. Tonsillotomy or tonsillectomy? A prospective study comparing histological and immunological findings in recurrent tonsillitis and tonsillar hyperplasia. European Archives of Oto‐Rhino‐Laryngology 2007;264:277‐84. - PubMed
Salmon 2006 {published data only}
-
- Salmon K, McGuigan F, Pereira JK. Brief report: optimizing children's memory and management of an invasive medical procedure: the influence of procedural narration and distraction. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2006;31(5):522‐7. - PubMed
Shapiro 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shapiro NL, Bhattacharyya N. Cold dissection versus coblation‐assisted adenotonsillectomy in children. Laryngoscope 2007;117(3):406‐10. - PubMed
Singh 2012 {published data only}
-
- Singh P. Effect of distraction techniques in behaviour responses to pain among toddlers receiving immunisation. Nursing Journal of India 2012;106(4):176‐79. - PubMed
Slater 2010 {published data only}
Slifer 2009 {published data only}
Sparks 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sparks LA, Setlik J, Luhman J. Parental holding and positioning to decrease IV distress in young children: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 2007;22(6):440‐7. - PubMed
Sundararajan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sundararajan L, Parikh DH. Evolving experience with video‐assisted thoracic surgery in congenital cystic lung lesions in a British pediatric center. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2007;42:1243‐50. - PubMed
Tanabe 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tanabe P, Ferket K, Thomas R, Paice J, Marcantonio R. The effect of standard care, ibuprofen, and distraction on pain relief and patient satisfaction in children with musculoskeletal trauma. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2002;28(2):118‐25. - PubMed
Ucar 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ucar S, Varma M, Altan S. The efficacy of non‐nutritive sucking and sucrose for the relief of pain during eye examinations for retinopathy of prematurity: a randomised controlled trial. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2014;99:A182‐A183.
Vignochi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vignochi C, Teixeira PP, Nader SS. Effect of aquatic physical therapy on pain and state of sleep and wakefulness among stable preterm newborns in neonatal intensive care units [Efeitos da fisioterapia aquatica na dor e no estado de sono e vigilia de recem‐nascidos pre‐termo estaveis internados em unidade de terapia intensiva neonatal]. Revista Brasileira de Fisioterapia (Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy) 2010;14(3):214‐20. - PubMed
Vivancos 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vivancos RBZ, Leite AM, Scochi CGS, dos Santos CB. The skin to skin contact at birth and newborn crying during vaccination against hepatitis B [O contato pele a pele ao nascimento e o choro de recem‐nascidos durante vacinacao contra Hepatite B]. Acta Paul Enferm 2010;23(4):461‐5.
Weissman 2009 {published data only}
Wisdorf‐Houtkooper 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wisdorf‐Houtkooper KK. The efficacy of pediatric pain management techniques for infants during inoculation procedures. Michigan: Western Michigan University, 1997.
Zeltzer 1991 {published data only}
-
- Zeltzer LK, Dolgin MJ, LeBaron S, LeBaron C. A randomized, controlled study of behavioral intervention for chemotherapy distress in children with cancer. Pediatrics 1991;88(1):34‐42. - PubMed
Zun 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zun L, Downey L. The use of cartoon distraction in the reduction of pain. Pain Practice 2012;12(s1):1‐199.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ho 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ho S, Ho L. Effects of facilitated swaddling for controlling procedural pain in premature neonates: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pain 2012;1:S59. [Author was contacted to get a copy of the article. There has not been a response to date]
Obeidat 2011 {published data only}
-
- Obeidat HM. The efficacy of containment for relieving painful responses among jordanian preterm infants during heel stick blood drawing. European Journal of Pain Supplements 2011;5(1):59. [Author was contacted to get a copy of the article. There has not been a response to date.]
Rozenfeld 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rozenfeld S, Mantin H, Mussafi H, Taizi T, Landau R, Kadosh D, et al. Effect of Snoezelen on pain perception and anxiety in CF infants during sputum suction. Pediatric Pulmonology 2012;47:41. [Author was contacted to get a copy of the article. There has not been a response to date.]
Taavoni 2013 {published data only}
-
- Taavoni S, Shahali S, Haghani H. Infants' vaccination pain management and effect of breast feeding, sucking the pacifier and mother's hug: A randomized control trial. European Psychiatry, Conference: 21st European Congress of Psychiatry 2013:28. [Author was contacted to get a copy of the article. There has not been a response to date.]
Additional references
Alexander 2003
-
- Alexander J, Manno M. Underuse of analgesia in very young pediatric patients with isolated painful injuries. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2003;41(5):617‐22. - PubMed
Anand 1987
-
- Anand KJS, Hickey PR. Pain and its effects in the human neonate and fetus. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;317(21):1321‐1329. - PubMed
Anand 2000
-
- Anand KJ. Pain, plasticity and premature birth: a prescription for permanent suffering?. Nature and Medicine 2000;6:971‐3. - PubMed
Anand 2001
-
- Anand KJS, International Evidence‐Based Group for Neonatal Pain. Consensus statement for the prevention and management of pain in the newborn. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2001;55(2):173‐80. - PubMed
Barber 2004
-
- Barber K. Pharmacology ‐ noun. The Canadian Oxford Dictionary ‐ Oxford Reference Online. University of Toronto Libraries: Oxford University Press, 2004.
Berde 2005
-
- Berde CB, Jaksic T, Lynn AM, Maxwell LG, Soriano SG, Tibboel D. Anesthesia and analgesia during and after surgery in neonates. Clinical Therapeutics 2005;27(6):900‐21. - PubMed
Bowlby 1982
-
- Bowlby J. Attachment. 2nd Edition. USA: Tavistock Institute of Human Relations, 1969/1982.
Brady‐Fryer 2009
Cepeda 2006
Chambless 2001
-
- Chambless DL, Ollendick TH. Empirically supported psychological interventions: controversies and evidence. Annual Review of Psychology 2001;52:685‐716. - PubMed
Cignacco 2007
-
- Cignacco E, Hamers JPH, Stoffel L, Lingen RA, Gessler P, McDougall J, et al. The efficacy of non‐pharmacological interventions in the management of procedural pain in preterm and term neonates. A systematic literature review. European Journal of Pain 2007;11(2):139‐52. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd Edition. Routledge, 1988.
Cohen 2008
Craig 2002
-
- Craig KD, Korol CT, Pillai RR. Challenges of judging pain in vulnerable infants. Clinics in Perinatology 2002;29:445‐58. - PubMed
Cyna 2010
Derbyshire 1999
-
- Derbyshire SWG. Locating the beginnings of pain. Bioethics 1999;13(1):1‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Field 1995
-
- Field T. Infancy is not without pain. Annals of Child Development 1995;10:1‐26.
Fitzgerald 2005
-
- Fitzgerald M. The development of nociceptive circuits. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2005;6:507‐20. - PubMed
Franck 2000
-
- Franck L, Greenberg C, Stevens B. Pain assessment in infants and children. Pediatric Clinics of North America 2000;47(3):487‐512. - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc) available from www.gradepro.org. GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool. McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc) available from www.gradepro.org, 2015.
Grunau 1987
-
- Grunau R, Craig KD. Pain expression in neonates: facial action and cry. Pain 1987;28(3):395‐410. - PubMed
Grunau 1996
-
- Grunau RVE, Whitfield M, Petrie JH. Children's judgments about pain at age 8‐10 years: do extremely low birthweight children (< 1000g) children differ from full birthweight peers?. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 1996;39(4):587‐94. - PubMed
Grunau 2000
-
- Grunau RE. Long‐term consequences of pain in human neonates. In: KJ Anand, BJ Stevens, PJ McGrath editor(s). Pain in Neonates, 2nd Edition. New York: Elsevier, 2000.
Harrison 2013
-
- Harrison D. Naturalistic studies of procedural pain management in infants – is it ethical to not provide pain management?. Pain 2013;154(9):1895‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Howard 2003
-
- Howard RF. Current status of pain management in children. JAMA 2003;290(18):2464‐9. - PubMed
IBM Corp 2012 [Computer program]
-
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp, 2012.
Johnston 1993
-
- Johnston CC, Stevens B, Craig KD, Grunau RV. Developmental changes in pain expression in premature, full‐term, two‐ and four‐month‐old infants. Pain 1993;52(2):201‐8. - PubMed
Johnston 2011
-
- Johnston CC, Fernandes AM, Campbell‐Yeo M. Pain in neonates is different. Pain 2011;152(3):S65‐S73. - PubMed
Johnston 2013b
Joint Committee 2000
-
- Joint Fetus and Newborn Committee of the Candian Paediatric Society and American Academy of Pediatrics. Prevention and management of pain and stress in the neonate. Pediatrics 2000;105(2):454‐61. - PubMed
Kleiber 1999
-
- Kleiber C, Harper D. Effects of distraction on children's pain and distress during medical procedures: a meta‐analysis. Nursing Research 1999;48(1):44‐9. - PubMed
McGraw 1943
-
- McGraw MD. The neuromuscular maturation of the human infant. New York: Columbia University Press, 1943.
Obeidat 2009
-
- Obeidat H, Kahalaf I, Callister LC, Froelicher ES. Use of facilitated tucking for nonpharmacological pain management in preterm infants: a systematic review. Journal of Perinatal and Neonatal Nursing 2009;23(4):372. - PubMed
Piira 2005
-
- Piira T, Sugiura T, Champion GD, Donnelly N, Cole ASJ. The role of parental presence in the context of children's medical procedures: a systematic review. Child: Care, Health and Development 2005;31(2):233‐43. - PubMed
Pillai Riddell 2005
-
- Pillai Riddell R, Stevens BJ, Katz J. Expanding the notion of chronic pain to infancy. Presentation at the Canadian Pain Society Annual Meeting. Pain Research & Management. 2005; Vol. 10:85.
Pillai Riddell 2009
Pillai Riddell 2013a
-
- Pillai Riddell RR, Racine N, Stevens BJ. Non‐pharmacological pain management in infancy. The Encyclopedia of Pain. Springer‐Verlag, 2013.
Pillai Riddell 2013b
-
- Pillai Riddell RR, Flora DB, Stevens SA, Stevens BJS, Cohen LL, Greenberg S, et al. Variability in infant acute pain responding meaningfully obscured by averaging pain responses. Pain 2013;154(5):714‐721. - PubMed
Pillai Riddell 2013c
-
- Pillai Riddell, RR. Invited commentary to “Naturalistic studies of procedural pain management in infants – is it ethical to not provide pain management?”. Pain 2013;154(9):1986‐1897. - PubMed
Pillai Riddell 2013d
-
- Pillai Riddell R, Racine N, Craig K, Campbell L. Psychological theories and biopsychosocial models in pediatric pain. In: P.J. McGrath, B. Stevens, S. Walker, W. Zempsky editor(s). Oxford Textbook of Pediatric Pain. London: Oxford, 2013:85‐94.
Prasopkittikun 2003
-
- Prasopkittikun T, Tilokskulchai F. Management of pain from heel stick in neonates ‐ an analysis of research conducted in Thailand. Journal of Perinatal and Neonatal Nursing 2003;17(4):304‐12. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schechter 2007
-
- Schechter NL, Zempsky WT, Cohen LL, McGrath PJ, McMurtry CM, Bright NS. Pain reduction during pediatric immunizations: Evidence‐based review and recommendations. Pediatrics 2007;119(5):184‐98. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shah 2009
Simons 2003
-
- Simons SHP, Dijk M, Anand KS, Roofthooft D, Lingen RA, Tibboel D. Do we still hurt newborn babies?: a prospective study of procedural pain and analgesia in neonates. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(11):1058‐64. - PubMed
Slifer 2002
-
- Slifer KJ, Tucker CL, Dahlquist LM. Helping children and caregivers cope with repeated invasive procedures: how are we doing?. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 2002;9(2):131‐52.
Stevens 1996
-
- Stevens B, Johnston C, Petryshen P, Taddio A. Premature infant pain profile: development and initial validation. Clinical Journal of Pain 1996;12:13‐22. - PubMed
Stevens 2007
-
- Stevens B, Pillai Riddell RR, Oberlander T, Gibbins S. Assessment of pain in neonates and infants. In: Anand KJ, Stevens BJ, McGrath PJ editor(s). Pain in Neonates and Infants. 3rd Edition. New York: Elsevier Limited, 2007.
Stevens 2010
Taddio 1997
-
- Taddio A, Katz J, Ilersich AL, Koren G. Effect of neonatal circumcision on pain response during subsequent routine vaccination. Lancet 1997;349(9052):599‐603. - PubMed
Taddio 2010
Taddio in press
-
- Taddio A, McMurtry MC, Shah V, Pillai Riddell R, Chambers CT, Noel M, et al. Clinical practice guideline (summary) for reducing pain during vaccination injections. Canadian Medical Association Journal In press.
Uman 2006
Yates 2005
-
- Yates SL, Morley S, Eccleston C, Williams AC. A scale for rating the quality of psychological trials for pain. Pain 2005;117:314‐25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

