Fate of HIV-1 cDNA intermediates during reverse transcription is dictated by transcription initiation site of virus genomic RNA
- PMID: 26631448
- PMCID: PMC4668388
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17680
Fate of HIV-1 cDNA intermediates during reverse transcription is dictated by transcription initiation site of virus genomic RNA
Abstract
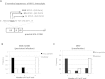
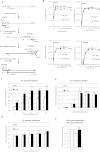
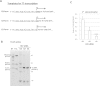
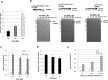
Retroviral reverse transcription is accomplished by sequential strand-transfers of partial cDNA intermediates copied from viral genomic RNA. Here, we revealed an unprecedented role of 5'-end guanosine (G) of HIV-1 genomic RNA for reverse transcription. Based on current consensus for HIV-1 transcription initiation site, HIV-1 transcripts possess a single G at 5'-ends (G1-form). However, we found that HIV-1 transcripts with additional Gs at 5'-ends (G2- and G3-forms) were abundantly expressed in infected cells by using alternative transcription initiation sites. The G2- and G3-forms were also detected in the virus particle, although the G1-form predominated. To address biological impact of the 5'-G number, we generated HIV clone DNA to express the G1-form exclusively by deleting the alternative initiation sites. Virus produced from the clone showed significantly higher strand-transfer of minus strong-stop cDNA (-sscDNA). The in vitro assay using synthetic HIV-1 RNAs revealed that the abortive forms of -sscDNA were abundantly generated from the G3-form RNA, but dramatically reduced from the G1-form. Moreover, the strand-transfer of -sscDNA from the G1-form was prominently stimulated by HIV-1 nucleocapsid. Taken together, our results demonstrated that the 5'-G number that corresponds to HIV-1 transcription initiation site was critical for successful strand-transfer of -sscDNA during reverse transcription.
Figures



References
-
- Cook P. R. A model for reverse transcription by a dimeric enzyme. The Journal of general virology 74, 691–697 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Sevilya Z., Loya S., Hughes S. H. & Hizi A. The ribonuclease H activity of the reverse transcriptases of human immunodeficiency viruses type 1 and type 2 is affected by the thumb subdomain of the small protein subunits. J Mol Biol 311, 957–971 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

