Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker
- PMID: 26631632
- PMCID: PMC4861144
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aac7071
Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker
Abstract
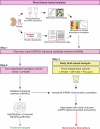
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects 8 to 16% people worldwide, with an increasing incidence and prevalence of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). The effective management of CKD is confounded by the inability to identify patients at high risk of progression while in early stages of CKD. To address this challenge, a renal biopsy transcriptome-driven approach was applied to develop noninvasive prognostic biomarkers for CKD progression. Expression of intrarenal transcripts was correlated with the baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in 261 patients. Proteins encoded by eGFR-associated transcripts were tested in urine for association with renal tissue injury and baseline eGFR. The ability to predict CKD progression, defined as the composite of ESKD or 40% reduction of baseline eGFR, was then determined in three independent CKD cohorts. A panel of intrarenal transcripts, including epidermal growth factor (EGF), a tubule-specific protein critical for cell differentiation and regeneration, predicted eGFR. The amount of EGF protein in urine (uEGF) showed significant correlation (P < 0.001) with intrarenal EGF mRNA, interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy, eGFR, and rate of eGFR loss. Prediction of the composite renal end point by age, gender, eGFR, and albuminuria was significantly (P < 0.001) improved by addition of uEGF, with an increase of the C-statistic from 0.75 to 0.87. Outcome predictions were replicated in two independent CKD cohorts. Our approach identified uEGF as an independent risk predictor of CKD progression. Addition of uEGF to standard clinical parameters improved the prediction of disease events in diverse CKD populations with a wide spectrum of causes and stages.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures



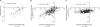

Comment in
-
Epidermal growth factor as a prognostic biomarker in chronic kidney diseases.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Oct;4(Suppl 1):S62. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.10.64. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27868030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez-Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo J-P, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nasseri K, Norman P, O'Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA, III, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Rodriguez De León F, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui-Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh P-H, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng Z-J, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Atkins R, Coresh J, Cohen EP, Collins AJ, Eckardt KU, Nahas ME, Jaber BL, Jadoul M, Levin A, Powe NR, Rossert J, Wheeler DC, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Chronic kidney disease as a global public health problem: Approaches and initiatives—A position statement from Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes. Kidney Int. 2007;72:247–259. - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Byrd-Holt D, Astor BC, Briggs JP, Eggers PW, Lacher DA, Hostetter TH. Chronic kidney disease awareness, prevalence, and trends among U.S. adults, 1999 to 2000. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005;16:180–188. - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY-M, Yang C-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382:260–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK081943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK083912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK092926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK079912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54DK083912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK083912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK079912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK100449/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR000433/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK081943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

