Design of a single protein that spans the entire 2-V range of physiological redox potentials
- PMID: 26631748
- PMCID: PMC4720346
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1515897112
Design of a single protein that spans the entire 2-V range of physiological redox potentials
Abstract
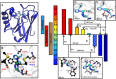
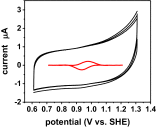
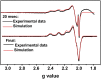
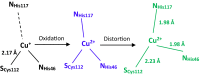
The reduction potential (E°') is a critical parameter in determining the efficiency of most biological and chemical reactions. Biology employs three classes of metalloproteins to cover the majority of the 2-V range of physiological E°'s. An ultimate test of our understanding of E°' is to find out the minimal number of proteins and their variants that can cover this entire range and the structural features responsible for the extreme E°'. We report herein the design of the protein azurin to cover a range from +970 mV to -954 mV vs. standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) by mutating only five residues and using two metal ions. Spectroscopic methods have revealed geometric parameters important for the high E°'. The knowledge gained and the resulting water-soluble redox agents with predictable E°'s, in the same scaffold with the same surface properties, will find wide applications in chemical, biochemical, biophysical, and biotechnological fields.
Keywords: azurin; cupredoxins; electron transfer; reduction potential; secondary coordination sphere.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
A single protein redox ruler.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jan 12;113(2):248-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522425112. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26676579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Beinert H, Holm RH, Münck E. Iron-sulfur clusters: Nature’s modular, multipurpose structures. Science. 1997;277(5326):653–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

