Prognostic Value of Ezrin in Various Cancers: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-analysis
- PMID: 26632332
- PMCID: PMC4668575
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17903
Prognostic Value of Ezrin in Various Cancers: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-analysis
Abstract
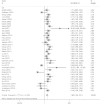
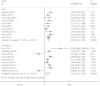
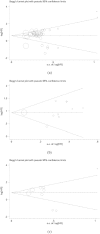
More and more studies have investigated the effects of Ezrin expression level on the prognostic role in various tumors. However, the results remain controversial rather than conclusive. Here, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the correlation of Ezrin expression with the prognosis in various tumors. the pooled hazard ratios (HR) with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated to evaluate the degree of the association. The overall results of fifty-five studies with 6675 patients showed that elevated Ezrin expression was associated with a worse prognosis in patients with cancers, with the pooled HRs of 1.86 (95% CI: 1.51-2.31, P < 0.001) for over survival (OS), 2.55 (95% CI: 2.14-3.05, P < 0.001) for disease-specific survival (DFS) and 2.02 (95% CI: 1.13-3.63, P = 0.018) for disease-specific survival (DSS)/metastasis-free survival (MFS) by the random, fixed and random effect model respectively. Similar results were also observed in the stratified analyses by tumor types, ethnicity background and sample source. This meta-analysis suggests that Ezrin may be a potential prognostic marker in cancer patients. High Ezrin is associated with a poor prognosis in a variety of solid tumors.
Figures


References
-
- Bretscher A., Reczek D. & Berryman M. Ezrin: a protein requiring conformational activation to link microfilaments to the plasma membrane in the assembly of cell surface structures. J. Cell Sc 110, 3011–3018 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Bretscher A., Edwards K. & Fehon R. G. ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat. Rev. Mol.Cell Bio l3, 586–599 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Gautreau A., Louvard D. & Arpin M. ERM proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical actin organization and cell growth signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Bio 14, 104–109 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Saotome I., Curto M. & McClatchey A. I. Ezrin is essential for epithelial organization and villus morphogenesis in the developing intestine. Dev. Cell 6, 855–864 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Sarrió D. et al. Abnormal Ezrin localization is associated with clinicopathological features in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. Trea 98, 71–79 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

