Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory Activity of Selaginellin Derivatives from Selaginella tamariscina
- PMID: 26633335
- PMCID: PMC6331899
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules201219774
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory Activity of Selaginellin Derivatives from Selaginella tamariscina
Abstract
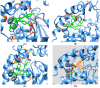
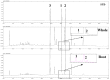
Selaginellin derivatives 1-3 isolated from Selaginella tamariscina were evaluated for their inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to demonstrate their potential for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. All selaginellin derivatives (1-3) inhibited sEH enzymatic activity and PHOME hydrolysis, in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 3.1 ± 0.1, 8.2 ± 2.2, and 4.2 ± 0.2 μM, respectively. We further determined that the derivatives function as non-competitive inhibitors. Moreover, the predicted that binding sites and interaction between 1-3 and sEH were solved by docking simulations. According to quantitative analysis, 1-3 were confirmed to have high content in the roots of S. tamariscina; among them, selaginellin 3 exhibited the highest content of 189.3 ± 0.0 μg/g.
Keywords: Selaginella tamariscina; Selaginellaceae; non-competitive inhibition; selaginellin; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shi S.-P., Wang Y.-Z., Zheng X.-K., Feng W.-S., Tu P.-F. Chemotaxonomic significance and biosynthesis of selaginellin from Selaginella tamariscina. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012;45:151–154. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2012.07.036. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

