Novel CAD-ALK gene rearrangement is drugable by entrectinib in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 26633560
- PMCID: PMC4701996
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.401
Novel CAD-ALK gene rearrangement is drugable by entrectinib in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Activated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions are recurrent events in a small fraction of colorectal cancers (CRCs), although these events have not yet been exploited as in other malignancies.
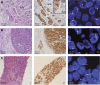
Methods: We detected ALK protein expression by immunohistochemistry and gene rearrangements by fluorescence in situ hybridisation in the ALKA-372-001 phase I study of the pan-Trk, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor entrectinib. One out of 487 CRCs showed ALK positivity with a peculiar pattern that prompted further characterisation by targeted sequencing using anchored multiplex PCR.
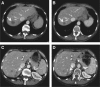
Results: A novel ALK fusion with the carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase (CAD) gene (CAD-ALK fusion gene) was identified. It resulted from inversion within chromosome 2 and the fusion of exons 1-35 of CAD with exons 20-29 of ALK. After failure of previous standard therapies, treatment of this patient with the ALK inhibitor entrectinib resulted in a durable objective tumour response.
Conclusions: We describe the novel CAD-ALK rearrangement as an oncogene and provide the first evidence of its drugability as a new molecular target in CRC.
Conflict of interest statement
ASB is a consultant/advisory member for Amgen, Bayer, and Merck-Serono. SS is a consultant/advisory member for Amgen, Bayer, Eli-Lilly, Merck-Serono, Merus, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Ignyta. DL, ZH, PM, DM, and RS are employees of Ignyta. AS, RB, EA, AG and AI are employees of Nerviano Medical Sciences. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aisner DL, Nguyen TT, Paskulin DD, Le AT, Haney J, Schulte N, Chionh F, Hardingham J, Mariadason J, Tebbutt N, Doebele RC, Weickhardt AJ, Varella-Garcia M (2014) ROS1 and ALK fusions in colorectal cancer, with evidence of intratumoral heterogeneity for molecular drivers. Mol Cancer Res 12: 111–118. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ardini E, Bosotti R, Borgia AL, De Ponti C, Somaschini A, Cammarota R, Amboldi N, Raddrizzani L, Milani A, Magnaghi P, Ballinari D, Casero D, Gasparri F, Banfi P, Avanzi N, Saccardo MB, Alzani R, Bandiera T, Felder E, Donati D, Pesenti E, Sartore-Bianchi A, Gambacorta M, Pierotti MA, Siena S, Veronese S, Galvani A, Isacchi A (2014) The TPM3-NTRK1 rearrangement is a recurring event in colorectal carcinoma and is associated with tumor sensitivity to TRKA kinase inhibition. Mol Oncol 8: 1495–1507. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ardini E, Meninchicheri M, Banfi P, Casero D, Giorgini ML, Saccardo MB, Amboldi N, Avanzi N, Orsini P, Isacchi A, Presenti E, Galvani A (2013) The ALK inhibitor NMS-E628 also potently inhibits ROS1 and induces tumor regression in ROS-driven models. Proceedings of the 104th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research 6–10 April 2013 Washington, DC, Cancer Res 73(8 Suppl): Abstract no. 2092.
-
- Bardelli A, Corso S, Bertotti A, Hobor S, Valtorta E, Siravegna G, Sartore-Bianchi A, Scala E, Cassingena A, Zecchin D, Apicella M, Migliardi G, Galimi F, Lauricella C, Zanon C, Perera T, Veronese S, Corti G, Amatu A, Gambacorta M, Diaz LA, Sausen M, Velculescu VE, Comoglio P, Trusolino L, Di Nicolantonio F, Giordano S, Siena S (2013) Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 3: 658–673. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

