Etanercept-associated myelitis
- PMID: 26634129
- PMCID: PMC4664838
- DOI: 10.1093/omcr/omv015
Etanercept-associated myelitis
Figures
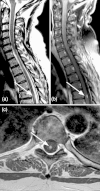
References
-
- Seror R, Richez C, Sordet C, Rist S, Gossec L, Direz G, et al. Pattern of demyelination occurring during anti-TNF-α therapy: a French national survey. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:868–874. - PubMed
-
- The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and The University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group. TNF neutralization in MS: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study. Neurology. 1999;53:457–465. - PubMed
-
- Van Oosten BW, Barkhof F, Truyen L, Boringa JB, Bertelsmann FW, von Blomberg BME, et al. Increased MRI activity and immune activation in two multiple sclerosis patients treated with the monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody cA2. Neurology. 1996;47:1531–1534. - PubMed
-
- Solomon AJ, Spain RI, Kruer MC, Bourdette D. Inflammatory neurological disease in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Mult Scler. 2011;17:1472–1487. - PubMed
-
- Tristano AG. Neurological adverse events associated with anti-tumor necrosis factor α treatment. J Neurol. 2010;257:1421–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

