MLLT1 YEATS domain mutations in clinically distinctive Favourable Histology Wilms tumours
- PMID: 26635203
- PMCID: PMC4686660
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10013
MLLT1 YEATS domain mutations in clinically distinctive Favourable Histology Wilms tumours
Abstract
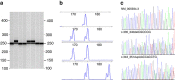
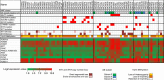
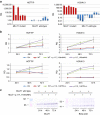
Wilms tumour is an embryonal tumour of childhood that closely resembles the developing kidney. Genomic changes responsible for the development of the majority of Wilms tumours remain largely unknown. Here we identify recurrent mutations within Wilms tumours that involve the highly conserved YEATS domain of MLLT1 (ENL), a gene known to be involved in transcriptional elongation during early development. The mutant MLLT1 protein shows altered binding to acetylated histone tails. Moreover, MLLT1-mutant tumours show an increase in MYC gene expression and HOX dysregulation. Patients with MLLT1-mutant tumours present at a younger age and have a high prevalence of precursor intralobar nephrogenic rests. These data support a model whereby activating MLLT1 mutations early in renal development result in the development of Wilms tumour.
Figures

References
-
- Rivera M. N. & Haber D. A. Wilms tumour: connecting tumorigenesis and organ development in the kidney. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 699–712 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Beckwith J. B., Kiviat N. B. & Bonadio J. F. Nephrogenic rests, nephroblastomatosis, and the pathogenesis of Wilms Tumour. Pediatr. Pathol. 10, 1–36 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Beckwith J. B. & Palmer N. F. Histopathology and prognosis of Wilms tumour. Results from the First National Wilms Tumour Study. Cancer 41, 1937–1948 (1978). - PubMed
-
- Bardeesy N. et al. Anaplastic Wilms tumour, a subtype displaying poor prognosis, harbours p53 gene mutations. Nat. Genet. 7, 91–97 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

