The global burden of injury: incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years and time trends from the Global Burden of Disease study 2013
- PMID: 26635210
- PMCID: PMC4752630
- DOI: 10.1136/injuryprev-2015-041616
The global burden of injury: incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years and time trends from the Global Burden of Disease study 2013
Abstract
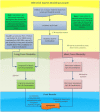
Background: The Global Burden of Diseases (GBD), Injuries, and Risk Factors study used the disability-adjusted life year (DALY) to quantify the burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. This paper provides an overview of injury estimates from the 2013 update of GBD, with detailed information on incidence, mortality, DALYs and rates of change from 1990 to 2013 for 26 causes of injury, globally, by region and by country.
Methods: Injury mortality was estimated using the extensive GBD mortality database, corrections for ill-defined cause of death and the cause of death ensemble modelling tool. Morbidity estimation was based on inpatient and outpatient data sets, 26 cause-of-injury and 47 nature-of-injury categories, and seven follow-up studies with patient-reported long-term outcome measures.
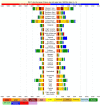
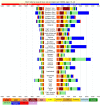
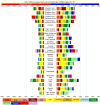
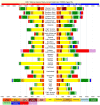
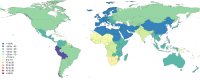
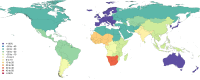
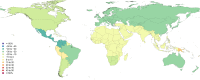
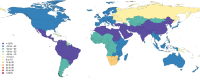
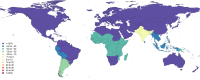
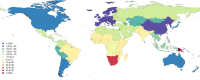
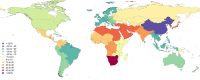
Results: In 2013, 973 million (uncertainty interval (UI) 942 to 993) people sustained injuries that warranted some type of healthcare and 4.8 million (UI 4.5 to 5.1) people died from injuries. Between 1990 and 2013 the global age-standardised injury DALY rate decreased by 31% (UI 26% to 35%). The rate of decline in DALY rates was significant for 22 cause-of-injury categories, including all the major injuries.
Conclusions: Injuries continue to be an important cause of morbidity and mortality in the developed and developing world. The decline in rates for almost all injuries is so prominent that it warrants a general statement that the world is becoming a safer place to live in. However, the patterns vary widely by cause, age, sex, region and time and there are still large improvements that need to be made.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
Comment in
-
Effect of injuries worldwide has fallen by almost a third since 1990.BMJ. 2015 Dec 3;351:h6548. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h6548. BMJ. 2015. PMID: 26637201 No abstract available.
References
-
- Worldbank. World development report 1993: investing in health. New York: Oxford University Press, 1993.
-
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD, Mathers CDE. Summary measures of population health: concepts, ethics, measurement and applications. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
