Lupus Nephritis IgG Induction of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV Expression in Podocytes and Alteration of Their Function
- PMID: 26636664
- PMCID: PMC6103450
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39499
Lupus Nephritis IgG Induction of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV Expression in Podocytes and Alteration of Their Function
Abstract
Objective: Kidney podocytes and their slit diaphragms prevent urinary protein loss. T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus display increased expression of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV). The present study was undertaken to investigate the role of CaMKIV in podocyte function in lupus nephritis (LN).
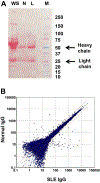
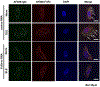
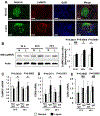
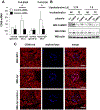
Methods: We treated kidney podocytes with IgG derived from healthy individuals or patients with LN and then analyzed gene expression using a DNA microarray. The localization of IgG in podocytes was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining, with or without silencing of neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). In addition, we silenced CAMK4 in podocytes and analyzed the expression of selected genes. We also examined the expression of CD86 in kidney podocytes from MRL/lpr, MRL/lpr.camkiv(-/-), and MRL/MPJ mice by in situ hybridization.
Results: We found that exposure of podocytes to IgG resulted in entry of IgG into the cytoplasm. IgG entered podocytes via the FcRn because less IgG was found in the cytoplasm of podocytes treated with FcRn small interfering RNA. DNA microarray studies of podocytes exposed to LN-derived IgG revealed up-regulation of genes related to the activation of immune cells or podocyte damage. Interestingly, CD86 expression decreased after silencing CAMK4 in podocytes. Also, in situ hybridization experiments showed that the expression of CD86 was reduced in podocytes from MRL/lpr.camkiv(-/-) mice.
Conclusion: LN-derived IgG enters podocytes and up-regulates CAMK4, which is followed by increased expression of genes known to be linked to podocyte damage and T cell activation. Targeted inhibition of CAMK4 in podocytes may prove to be clinically useful in patients with LN.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2011; 365:2110–21. - PubMed
-
- Kraft SW, Schwartz MM, Korbet SM, Lewis EJ. Glomerular podocytopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:175–9. - PubMed
-
- Trivedi S, Zeier M, Reiser J. Role of podocytes in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2009;24:3607–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

