Somatic mtDNA variation is an important component of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 26639157
- PMCID: PMC4759607
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.036
Somatic mtDNA variation is an important component of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
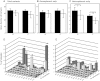
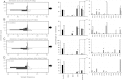
There is a growing body of evidence linking mitochondrial dysfunction, mediated either through inherited mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variation or mitochondrial proteomic deficit, to Parkinson's disease (PD). Yet, despite this, the role of somatic mtDNA point mutations and specifically point-mutational burden in PD is poorly understood. Here, we take advantage of recent technical and methodological advances to examine the role of age-related and acquired mtDNA mutation in the largest study of mtDNA in postmortem PD tissue to date. Our data show that PD patients suffer an increase in mtDNA mutational burden in, but no limited to, the substantia nigra pars compacta when compared to matched controls. This mutational burden appears increased in genes encoding cytochrome c oxidase, supportive of previous protein studies of mitochondrial dysfunction in PD. Accepting experimental limitations, our study confirms the important role of age-related mtDNA point mutation in the etiology of PD, moreover, by analyzing 2 distinct brain regions, we are able to show that PD patient brains are more vulnerable to mtDNA mutation overall.
Keywords: Mitochondria; Neurodegeneration; Parkinson's disease; Somatic mutation.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aksenov M.Y., Tucker H.M., Nair P., Aksenova M.V., Butterfield D.A., Estus S., Markesbery W.R. The expression of several mitochondrial and nuclear genes encoding the subunits of electron transport chain enzyme complexes, cytochrome c oxidase, and NADH dehydrogenase, in different brain regions in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem. Res. 1999;24:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Belle E.M.S., Piganeau G., Gardner M., Eyre-Walker A. An investigation of the variation in the transition bias among various animal mitochondrial DNA. Gene. 2005;355:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Bender A., Krishnan K.J., Morris C.M., Taylor G.A., Reeve A.K., Perry R.H., Jaros E., Hersheson J.S., Betts J., Klopstock T., Taylor R.W., Turnbull D.M. High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:515–517. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Del Tredici K., Rub U., de Vos R.A.I., Steur E.N.H.J., Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2003;24:197–211. - PubMed
-
- Cantuti-Castelvetri I., Lin M.T., Zheng K., Keller-McGandy C.E., Betensky R.A., Johns D.R., Beal M.F., Standaert D.G., Simon D.K. Somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in single neurons and glia. Neurobiol. Aging. 2005;26:1343–1355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

