Human keratinocytes have two interconvertible modes of proliferation
- PMID: 26641719
- PMCID: PMC4872834
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3282
Human keratinocytes have two interconvertible modes of proliferation
Abstract
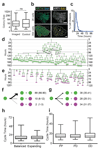
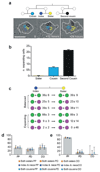
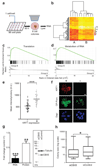
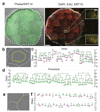
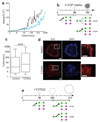
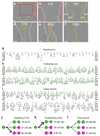
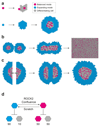
Single stem cells, including those in human epidermis, have a remarkable ability to reconstitute tissues in vitro, but the cellular mechanisms that enable this are ill-defined. Here we used live imaging to track the outcome of thousands of divisions in clonal cultures of primary human epidermal keratinocytes. Two modes of proliferation were seen. In 'balanced' mode, similar proportions of proliferating and differentiating cells were generated, achieving the 'population asymmetry' that sustains epidermal homeostasis in vivo. In 'expanding' mode, an excess of cycling cells was produced, generating large expanding colonies. Cells in expanding mode switched their behaviour to balanced mode once local confluence was attained. However, when a confluent area was wounded in a scratch assay, cells near the scratch switched back to expanding mode until the defect was closed. We conclude that the ability of a single epidermal stem cell to reconstitute an epithelium is explained by two interconvertible modes of proliferation regulated by confluence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rheinwald JG, Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975;6:331–343. - PubMed
-
- Watt FM, Green H. Stratification and terminal differentiation of cultured epidermal cells. Nature. 1982;295:434–436. - PubMed
-
- Sato T, Clevers H. Growing self-organizing mini-guts from a single intestinal stem cell: mechanism and applications. Science. 2013;340:1190–1194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 17257/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 090334/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12022/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 97922/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0700600/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

