'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment
- PMID: 26641934
- PMCID: PMC4718764
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1979
'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment
Abstract
Biocontainment systems that couple environmental sensing with circuit-based control of cell viability could be used to prevent escape of genetically modified microbes into the environment. Here we present two engineered safeguard systems known as the 'Deadman' and 'Passcode' kill switches. The Deadman kill switch uses unbalanced reciprocal transcriptional repression to couple a specific input signal with cell survival. The Passcode kill switch uses a similar two-layered transcription design and incorporates hybrid LacI-GalR family transcription factors to provide diverse and complex environmental inputs to control circuit function. These synthetic gene circuits efficiently kill Escherichia coli and can be readily reprogrammed to change their environmental inputs, regulatory architecture and killing mechanism.
Figures
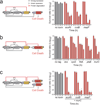
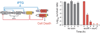

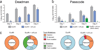
Comment in
-
Synthetic biology: Genetic kill switches--a matter of life or death.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Feb;17(2):67. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.29. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26688199 No abstract available.
-
Synthetic biology: Building genetic containment.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Feb;12(2):55-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2004. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26784843 No abstract available.
References
METHODS ONLY-REFERENCES
-
- Larkin MA, et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–2948. - PubMed
-
- Bell CE, Lewis M. A closer view of the conformation of the Lac repressor bound to operator. Nature structural biology. 2000;7:209–214. - PubMed
-
- Friedman AM, Fischmann TO, Steitz TA. Crystal structure of lac repressor core tetramer and its implications for DNA looping. Science. 1995;268:1721–1727. - PubMed
-
- Lewis M, et al. Crystal structure of the lactose operon repressor and its complexes with DNA and inducer. Science. 1996;271:1247–1254. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher MA, Choi KY, Lu F, Zalkin H, Brennan RG. Mechanism of corepressor-mediated specific DNA binding by the purine repressor. Cell. 1995;83:147–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

