HDL signaling and protection against coronary artery atherosclerosis in mice
- PMID: 26642235
- PMCID: PMC4820886
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.30.20150079
HDL signaling and protection against coronary artery atherosclerosis in mice
Abstract
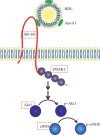
Atherosclerosis is a leading underlying factor in cardiovascular disease and stroke, important causes of morbidity and mortality across the globe. Abundant epidemiological studies demonstrate that high levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) are associated with reduced risk of atherosclerosis and preclinical, animal model studies demonstrate that this association is causative. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of HDL will allow more strategic approaches to development of HDL based therapeutics. Recent evidence suggests that an important aspect of the ability of HDL to protect against atherosclerosis is its ability to trigger signaling responses in a variety of target cells including endothelial cells and macrophages in the vessel wall. These signaling responses require the HDL receptor, scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1), an adaptor protein (PDZK1) that binds to the cytosolic C terminus of SR-B1, Akt1 activation and (at least in endothelial cells) activation of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS). Mouse models of atherosclerosis, exemplified by apolipoprotein E or low density lipoprotein receptor gene inactivated mice (apoE or LDLR KO) develop atherosclerosis in their aortas but appear generally resistant to coronary artery atherosclerosis. On the other hand, inactivation of each of the components of HDL signaling (above) in either apoE or LDLR KO mice renders them susceptible to extensive coronary artery atherosclerosis suggesting that HDL signaling may play an important role in protection against coronary artery disease.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; high density lipoprotein; myocardial infarction; scavenger receptor class B type 1.
© 2016 by the Journal of Biomedical Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CLC number: R714.252, Document code: A
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein A1 Protects Against Necrotic Core Development in Atherosclerotic Plaques: PDZK1-Dependent High-Density Lipoprotein Suppression of Necroptosis in Macrophages.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Jan;43(1):45-63. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.318062. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023. PMID: 36353992 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin Reduces Aortic Sinus and Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis in SR-B1 (Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1)/ApoE (Apolipoprotein E) Double Knockout Mice Independently of Plasma Cholesterol Lowering.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Jan;38(1):26-39. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.305140. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29162602 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of diet on occlusive coronary artery atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in scavenger receptor class B, type 1/low-density lipoprotein receptor double knockout mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Nov;34(11):2394-403. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304200. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25212235
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
Scavenger receptor class B type I in high-density lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and heart disease: lessons from gene-targeted mice.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Feb;32(Pt 1):116-20. doi: 10.1042/bst0320116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 14748727 Review.
Cited by
-
From Classical to Unconventional: The Immune Receptors Facilitating Platelet Responses to Infection and Inflammation.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;9(10):343. doi: 10.3390/biology9100343. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do the Apoe-/- and Ldlr-/- Mice Yield the Same Insight on Atherogenesis?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1734-41. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.306874. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27386935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein A1 deficiency increases macrophage apoptosis and necrotic core development in atherosclerotic plaques in a Bim-dependent manner.J Lipid Res. 2025 May;66(5):100782. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100782. Epub 2025 Mar 20. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 40120762 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Exploration of Paraoxonase 1 Function in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7764. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097764. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in vascular physiology and pathophysiology: estrogen and androgen signaling in health and disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):H524-H545. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00217.2016. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28626075 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krieger M. Lipoprotein receptor SR-BI[J]. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:523–558. - PubMed
-
- Brodde MF, Korporaal SJ, Herminghaus G, et al. Native high-density lipoproteins inhibit platelet activation via scavenger receptor BI: role of negatively charged phospholipids[J]. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215:374–382. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

