Loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3 leading to A20 haploinsufficiency cause an early-onset autoinflammatory disease
- PMID: 26642243
- PMCID: PMC4777523
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3459
Loss-of-function mutations in TNFAIP3 leading to A20 haploinsufficiency cause an early-onset autoinflammatory disease
Abstract
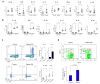
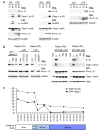
Systemic autoinflammatory diseases are driven by abnormal activation of innate immunity. Herein we describe a new disease caused by high-penetrance heterozygous germline mutations in TNFAIP3, which encodes the NF-κB regulatory protein A20, in six unrelated families with early-onset systemic inflammation. The disorder resembles Behçet's disease, which is typically considered a polygenic disorder with onset in early adulthood. A20 is a potent inhibitor of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Mutant, truncated A20 proteins are likely to act through haploinsufficiency because they do not exert a dominant-negative effect in overexpression experiments. Patient-derived cells show increased degradation of IκBα and nuclear translocation of the NF-κB p65 subunit together with increased expression of NF-κB-mediated proinflammatory cytokines. A20 restricts NF-κB signals via its deubiquitinase activity. In cells expressing mutant A20 protein, there is defective removal of Lys63-linked ubiquitin from TRAF6, NEMO and RIP1 after stimulation with tumor necrosis factor (TNF). NF-κB-dependent proinflammatory cytokines are potential therapeutic targets for the patients with this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures



References
-
- van Kempen TS, Wenink MH, Leijten EF, Radstake TR, Boes M. Perception of self: distinguishing autoimmunity from autoinflammation. Nature reviews Rheumatology. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behcet’s disease. The New England journal of medicine. 1999;341:1284–91. - PubMed
-
- Catrysse L, Vereecke L, Beyaert R, van Loo G. A20 in inflammation and autoimmunity. Trends in immunology. 2014;35:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Russo RA, Brogan PA. Monogenic autoinflammatory diseases. Rheumatology. 2014;53:1927–39. - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Aksentijevich I. New players driving inflammation in monogenic autoinflammatory diseases. Nature reviews. Rheumatology. 2015;11:11– 20. - PubMed
Methods-only references
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

